Maternal inheritance of functional centrioles in two parthenogenetic nematodes
- PMID: 39025889
- PMCID: PMC11258339
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50427-5
Maternal inheritance of functional centrioles in two parthenogenetic nematodes
Abstract
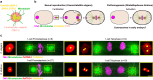
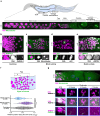
Centrioles are the core constituent of centrosomes, microtubule-organizing centers involved in directing mitotic spindle assembly and chromosome segregation in animal cells. In sexually reproducing species, centrioles degenerate during oogenesis and female meiosis is usually acentrosomal. Centrioles are retained during male meiosis and, in most species, are reintroduced with the sperm during fertilization, restoring centriole numbers in embryos. In contrast, the presence, origin, and function of centrioles in parthenogenetic species is unknown. We found that centrioles are maternally inherited in two species of asexual parthenogenetic nematodes and identified two different strategies for maternal inheritance evolved in the two species. In Rhabditophanes diutinus, centrioles organize the poles of the meiotic spindle and are inherited by both the polar body and embryo. In Disploscapter pachys, the two pairs of centrioles remain close together and are inherited by the embryo only. Our results suggest that maternally-inherited centrioles organize the embryonic spindle poles and act as a symmetry-breaking cue to induce embryo polarization. Thus, in these parthenogenetic nematodes, centrioles are maternally-inherited and functionally replace their sperm-inherited counterparts in sexually reproducing species.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 GM117407/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM129325/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM130764/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- ERC-CoG ChromoSOMe 819179/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

