High flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy versus non-invasive ventilation for acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with acute-moderate hypercapnic respiratory failure: a randomized controlled non-inferiority trial
- PMID: 39026242
- PMCID: PMC11264824
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-024-05040-9
High flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy versus non-invasive ventilation for acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with acute-moderate hypercapnic respiratory failure: a randomized controlled non-inferiority trial
Abstract
Background: Although cumulative studies have demonstrated a beneficial effect of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen (HFNC) in acute hypercapnic respiratory failure, randomized trials to compare HFNC with non-invasive ventilation (NIV) as initial treatment in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD) patients with acute-moderate hypercapnic respiratory failure are limited. The aim of this randomized, open label, non-inferiority trial was to compare treatment failure rates between HFNC and NIV in such patients.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with AECOPD with a baseline arterial blood gas pH between 7.25 and 7.35 and PaCO2 ≥ 50 mmHg admitted to two intensive care units (ICUs) at a large tertiary academic teaching hospital between March 2018 and December 2022 were randomly assigned to HFNC or NIV. The primary endpoint was the rate of treatment failure, defined as endotracheal intubation or a switch to the other study treatment modality. Secondary endpoints were rates of intubation or treatment change, blood gas values, vital signs at one, 12, and 48 h, 28-day mortality, as well as ICU and hospital lengths of stay.
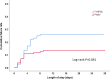
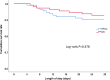
Results: 225 total patients (113 in the HFNC group and 112 in the NIV group) were included in the intention-to-treat analysis. The failure rate of the HFNC group was 25.7%, while the NIV group was 14.3%. The failure rate risk difference between the two groups was 11.38% (95% CI 0.25-21.20, P = 0.033), which was higher than the non-inferiority cut-off of 9%. In the per-protocol analysis, treatment failure occurred in 28 of 110 patients (25.5%) in the HFNC group and 15 of 109 patients (13.8%) in the NIV group (risk difference, 11.69%; 95% CI 0.48-22.60). The intubation rate in the HFNC group was higher than in the NIV group (14.2% vs 5.4%, P = 0.026). The treatment switch rate, ICU and hospital length of stay or 28-day mortality in the HFNC group were not statistically different from the NIV group (all P > 0.05).
Conclusion: HFNC was not shown to be non-inferior to NIV and resulted in a higher incidence of treatment failure than NIV when used as the initial respiratory support for AECOPD patients with acute-moderate hypercapnic respiratory failure.
Trial registration: chictr.org (ChiCTR1800014553). Registered 21 January 2018, http://www.chictr.org.cn.
Keywords: Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases; High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy; Non-invasive ventilation; Randomized controlled trial; Respiratory failure.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Probing the efficacy of high-flow nasal cannula in the treatment of acute exacerbations of COPD with acute-moderate hypercapnic respiratory failure.Crit Care. 2024 Aug 5;28(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-05050-7. Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 39103951 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
High flow nasal cannula versus non-invasive ventilation in the treatment of acute exacerbations of COPD with acute-moderate hypercapnic respiratory failure.Crit Care. 2024 Sep 19;28(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-05094-9. Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 39300587 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bruni A, Garofalo E, Pelaia C, Messina A, Cammarota G, Murabito P, et al. Patient-ventilator asynchrony in adult critically ill patients. Minerva Anestesiol Italy. 2019;85(6):676–88. - PubMed
-
- Spoletini G, Cortegiani A, Gregoretti C. Physiopathological rationale of using high-flow nasal therapy in the acute and chronic setting: a narra tive review. Trends Anaesth Crit Care. 2019;26–27:22–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

