SKN-1 isoform-c is essential for C. elegans development
- PMID: 39027732
- PMCID: PMC11255869
- DOI: 10.17912/micropub.biology.001205
SKN-1 isoform-c is essential for C. elegans development
Abstract
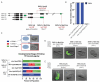
The transcription factor SKN-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans is a critical regulator of various biological processes, impacting development, diet and immune responses, cellular detoxification, and lipid metabolism; thereby playing a pivotal role in regulating the health and lifespan of the organism. The primary isoforms of SKN-1 ( SKN-1 a, SKN-1 b, and SKN-1 c) exhibit distinct functions resembling mammalian Nrf transcription factors. This study investigates the specific role of the SKN-1 c isoform in development by generating mutants with targeted missense mutations in the skn-1 c and skn-1 a isoforms. The skn-1 c Met1Ala mutants, which replaces a start methionine with alanine, renders SKN-1 c non-functional while preserving other isoforms, produced inviable embryos, requiring a balancer chromosome for proper embryonic development. In contrast, skn-1 a Met1Ala mutants, which replaces the start methionine with alanine for this isoform, displayed normal embryonic development and hatching. Moreover, the data suggest that SKN-1 c plays a crucial role in embryonic development, as strains without maternally deposited SKN-1 c lead to embryos that are developmentally arrested. Together, these findings contribute to our understanding of SKN-1 c's specific role in influencing embryogenesis and development in C. elegans.
Copyright: © 2024 by the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest present.
Figures
References
-
- Bishop NA, Guarente L. Two neurons mediate diet-restriction-induced longevity in C. elegans. Nature. 2007;447(7144):545-549. - PubMed
-
- Bowerman B, Draper BW, Mello CC, Priess JR. The maternal gene skn-1 encodes a protein that is distributed unequally in early C. elegans embryos. Cell. 1993;74(3):443-452. - PubMed
-
- Bowerman B, Eaton BA, Priess JR. skn-1, a maternally expressed gene required to specify the fate of ventral blastomeres in the early C. elegans embryo. Cell. 1992;68(6):1061-1075. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
