Role of Health Care Professionals in the Success of Blood Pressure Control Interventions in Patients With Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39027934
- PMCID: PMC11338746
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.123.010396
Role of Health Care Professionals in the Success of Blood Pressure Control Interventions in Patients With Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Globally, only 13.8% of patients with hypertension have their blood pressure (BP) controlled. Trials testing interventions to overcome barriers to BP control have produced mixed results. Type of health care professional delivering the intervention may play an important role in intervention success. The goal of this meta-analysis is to determine which health care professionals are most effective at delivering BP reduction interventions.
Methods: We searched Medline and Embase (until December 2023) for randomized controlled trials of interventions targeting barriers to hypertension control reporting who led intervention delivery. One hundred articles worldwide with 116 comparisons and 90 474 participants with hypertension were included. Trials were grouped by health care professional, and the effects of the intervention on systolic and diastolic BP were combined using random effects models and generalized estimating equations.
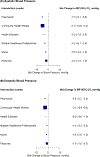
Results: Pharmacist-led interventions , community health worker-led interventions, and health educator-led interventions resulted in the greatest systolic BP reductions of -7.3 (95% CI, -9.1 to -5.6), -7.1 (95% CI, -10.8 to -3.4), and -5.2 (95% CI, -7.8 to -2.6) mm Hg, respectively. Interventions led by multiple health care professionals, nurses, and physicians also resulted in significant systolic BP reductions of -4.2 (95% CI, -6.1 to -2.4), -3.0 (95% CI, -4.2 to -1.9), and -2.4 (95% CI, -3.4 to -1.5) mm Hg, respectively. Similarly, the greatest diastolic BP reductions were -3.9 (95% CI, -5.2 to -2.5) mm Hg for pharmacist-led and -3.7 (95% CI, -6.6 to -0.8) mm Hg for community health worker-led interventions. In pairwise comparisons, pharmacist were significantly more effective than multiple health care professionals, nurses, and physicians at delivering interventions.
Conclusions: Pharmacists and community health workers are most effective at leading BP intervention implementation and should be prioritized in future hypertension control efforts.
Keywords: blood pressure; cardiovascular diseases; health personnel; hypertension; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Comment in
-
Pharmacist's Role in the Success of Blood Pressure Control Interventions: Evidence Isn't the Barrier….Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2024 Aug;17(8):e011175. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.124.011175. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2024. PMID: 39027935 No abstract available.
References
-
- Stanaway JD, Afshin A, Gakidou E, Lim SS, Abate D, Abate KH, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1923–1994. - PMC - PubMed
-
- GBD Causes of Death Collaborators, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, Abdela J, Abdelalim A, et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1736–1788. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Borzecki AM, Oliveria SA, Berlowitz DR. Barriers to hypertension control. American Heart Journal. 2005;149:785–794. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

