Phase II Trial of HER-Vaxx, a B-cell Peptide-Based Vaccine, in HER2-Overexpressing Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients Under Platinum-Based Chemotherapy (HERIZON)
- PMID: 39028916
- PMCID: PMC11393538
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0742
Phase II Trial of HER-Vaxx, a B-cell Peptide-Based Vaccine, in HER2-Overexpressing Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients Under Platinum-Based Chemotherapy (HERIZON)
Abstract
Purpose: A multicenter, randomized, open-label, phase II study (HERIZON; NCT02795988) was conducted to evaluate the clinical and immunologic efficacy of HER-Vaxx (IMU-131), a B-cell, peptide-based vaccine targeting HER2 overexpressed in 6% to 30% of gastroesophageal adenocarcinomas (GEA).
Patients and methods: Patients (n = 36) with GEA were treated with standard-of-care chemotherapy (n = 17) or HER-Vaxx plus chemotherapy (n = 19), using the recommended phase 2 dose for the vaccine. Overall survival (OS; primary endpoint), safety, progression-free survival (PFS), clinical response (secondary endpoints), and vaccine-induced HER2-specific antibody levels in serum and correlation with tumor response rates (exploratory endpoints) were investigated.
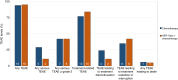
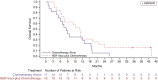
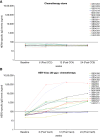
Results: A 40% OS benefit [HR, 0.60; median OS, 13.9 months; 80% confidence interval (CI), 7.52-14.32] for patients treated with HER-Vaxx plus chemotherapy compared with OS of 8.31 months (80% CI, 6.01-9.59) in patients that received chemotherapy alone. A 20% PFS difference was obtained for the vaccination arm (HR, 0.80; 80% CI, 0.47, 1.38). No additional toxicity due to HER-Vaxx was observed. The vaccine-induced high levels of HER2-specific total IgG and IgG1 antibodies (P < 0.001 vs. controls) that significantly correlated with tumor reduction (IgG, P = 0.001; IgG1, P = 0.016), had a significant capacity in inhibiting phosphorylation of the intracellular HER2-signaling pathways, mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, and decreased immunosuppressive FOXP3+ regulatory T cells.
Conclusions: HER-Vaxx plus standard chemotherapy exhibits an excellent safety profile and improves OS. Furthermore, vaccine-induced immune response was significantly associated with reduced tumor size compared with standard-of-care chemotherapy. The presented vaccination approach may substitute for treatment with trastuzumab, upon unavailability or toxicity, based on further evidence of equivalent treatment efficacy.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
C. C. Zielinski reports consulting fees from Athenex, MSD, Imugene Limited (until September 2018), AstraZeneca, Servier, and Eli Lilly and institutional fees from Eli Lilly, BMS, MSD, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Merck, Amgen, Servier, Takeda, Daiichi Roche, Boehringer, Celgene, and Halozyme. L. M. O. Chong reports leadership fees from Imugene Limited. B. Nixon reports employment from and is a shareholder/stockholder of Imugene Limited. N. J. Ede reports employment at Imugene Limited. S. Yavrom reports employment at Imugene Limited. M. Kundi reports consultation fees from BlueSky Immunotherapies and Pfizer (funding to institute). U. Wiedermann reports consulting fees from Imugene Limited (until September 2018) and funding to the institute from GSK, Pfizer, and Themis. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures


References
-
- Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001;2:127–37. - PubMed
-
- Bang Y-J, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010;376:687–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

