Lysine L-lactylation is the dominant lactylation isomer induced by glycolysis
- PMID: 39030363
- PMCID: PMC11666458
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-024-01680-8
Lysine L-lactylation is the dominant lactylation isomer induced by glycolysis
Abstract
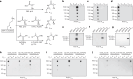
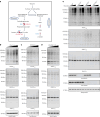
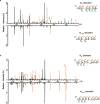
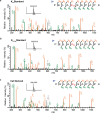
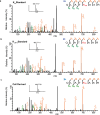
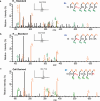
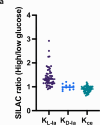
Lysine L-lactylation (Kl-la) is a novel protein posttranslational modification (PTM) driven by L-lactate. This PTM has three isomers: Kl-la, N-ε-(carboxyethyl)-lysine (Kce) and D-lactyl-lysine (Kd-la), which are often confused in the context of the Warburg effect and nuclear presence. Here we introduce two methods to differentiate these isomers: a chemical derivatization and high-performance liquid chromatography analysis for efficient separation, and isomer-specific antibodies for high-selectivity identification. We demonstrated that Kl-la is the primary lactylation isomer on histones and dynamically regulated by glycolysis, not Kd-la or Kce, which are observed when the glyoxalase system was incomplete. The study also reveals that lactyl-coenzyme A, a precursor in L-lactylation, correlates positively with Kl-la levels. This work not only provides a methodology for distinguishing other PTM isomers, but also highlights Kl-la as the primary responder to glycolysis and the Warburg effect.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Y.Z. is a founder, board member or advisor to and inventor on patents licensed to PTM Bio Inc. (Hangzhou, China and Chicago, IL, USA) and Maponos Therapeutics Inc. (Chicago, IL, USA). The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Allis, C. D. & Jenuwein, T. The molecular hallmarks of epigenetic control. Nat. Rev. Genet.17, 487–500 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Walsh, C. T., Garneau-Tsodikova, S. & Gatto, G. J. Jr. Protein posttranslational modifications: the chemistry of proteome diversifications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.44, 7342–7372 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA251677/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01GM132261/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 CA251677/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK071801/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10RR029531/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- S10OD028473/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 DK071801/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AR078555/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 AR078555/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG052324/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 GM132261/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028473/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG052324/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CoG-725172/European Science Foundation (ESF)
- CHE-2108223/National Science Foundation (NSF)
- S10 RR029531/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK071801/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- RF1 AG052324/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 32270822/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

