Comparative speed of kill provided by lotilaner (Credelio™), sarolaner (Simparica Trio™), and afoxolaner (NexGard™) to control Amblyomma americanum infestations on dogs
- PMID: 39030610
- PMCID: PMC11264992
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-024-06363-w
Comparative speed of kill provided by lotilaner (Credelio™), sarolaner (Simparica Trio™), and afoxolaner (NexGard™) to control Amblyomma americanum infestations on dogs
Abstract
Background: Canine acaricides with rapid onset and sustained activity can reduce pathogen transmission risk and enhance pet owner experience. This randomized, complete block design, investigator-masked study compared the speed of kill of Amblyomma americanum provided by three monthly-use isoxazoline-containing products.
Methods: Eight randomized beagles per group were treated (day 0), per label, with sarolaner (combined with moxidectin and pyrantel, Simparica Trio™), afoxolaner (NexGard™), or lotilaner (Credelio™), or remained untreated. Infestations with 50 adult A. americanum were conducted on days - 7, - 2, 21, and 28, and tick counts were performed on day - 5 (for blocking), and at 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h following treatment and subsequent infestations. Efficacy calculations were based on geometric mean live tick counts. A linear mixed model was used for between-group comparisons.
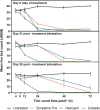
Results: On day 0, only lotilaner significantly reduced an A. americanum infestation by 12 h (43.3%; P = 0.002). Efficacy of lotilaner and afoxolaner at 24 h post-treatment was 95.3% and 97.6%, respectively, both significantly different from sarolaner (74%) (P = 0.002, P < 0.001, respectively). On day 21, at 12 h postinfestation, lotilaner efficacy (59.6%) was significantly different from sarolaner (0.0%) (P < 0.001) and afoxolaner (6.3%) (P < 0.001). At 24 h, lotilaner efficacy (97.4%) was significantly different (P < 0.001) from sarolaner and afoxolaner (13.6% and 14.9%, respectively). On day 28, at 12 h postinfestation, lotilaner efficacy (47.8%) was significantly different from sarolaner (17.1%) (P = 0.020) and afoxolaner (9.0%) (P = 0.006). At 24 h, lotilaner efficacy (92.3%) was significantly different from sarolaner 4.9% (P < 0.001) and afoxolaner (0.0%) (P < 0.001). Speed of kill for sarolaner and afoxolaner, but not lotilaner, significantly declined over the study period. Following reinfestation on day 28, neither sarolaner nor afoxolaner reached 90% efficacy by 48 h. By 72 h, sarolaner efficacy was 97.4% and afoxolaner efficacy was 86.3%. Only lotilaner achieved ≥ 90% efficacy by 24 h post-treatment and 24 h postinfestation on days 21 and 28. Time to ≥ 90% efficacy following new infestations consistently occurred 24-48 h earlier for lotilaner compared with sarolaner or afoxolaner.
Conclusions: Credelio (lotilaner) has a more rapid onset of acaricidal activity against A. americanum than Simparica Trio (sarolaner-moxidectin-pyrantel) and NexGard (afoxolaner). Only lotilaner's speed of tick kill is sustained throughout the dosing period.
Keywords: Amblyomma americanum; Afoxolaner; Canine; Credelio; Dog; Lone star tick; Lotilaner; NexGard; Sarolaner; Simparica Trio.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
K.E.R., M.W.D., and B.H.H. are paid consultants for several animal health companies including Elanco Animal Health and Boehringer Ingelheim. T.M.K. and J.C.N. are employees of Elanco Animal Health. W.G.R. and M.C.B. are paid consultants for Elanco Animal Health. J.R.J.J.C. is an Associate Editor of Parasites and Vectors and is a paid consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim. A portion of K.R.M. and C.J.S. graduate program is funded by Elanco Animal Health.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

