Determining M2 macrophages content for the anti-tumor effects of metal-organic framework-encapsulated pazopanib nanoparticles in breast cancer
- PMID: 39033109
- PMCID: PMC11264935
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02694-z
Determining M2 macrophages content for the anti-tumor effects of metal-organic framework-encapsulated pazopanib nanoparticles in breast cancer
Abstract
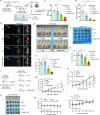
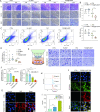
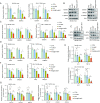
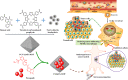
Pazopanib (PAZ), an oral multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor, demonstrates promising cytostatic activities against various human cancers. However, its clinical utility is limited by substantial side effects and therapeutic resistance. We developed a nanoplatform capable of delivering PAZ for enhanced anti-breast cancer therapy. Nanometer-sized PAZ@Fe-MOF, compared to free PAZ, demonstrated increased anti-tumor therapeutic activities in both syngeneic murine 4T1 and xenograft human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer models. High-throughput single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) revealed that PAZ@Fe-MOF significantly reduced pro-tumorigenic M2-like macrophage populations at tumor sites and suppressed M2-type signaling pathways, such as ATF6-TGFBR1-SMAD3, as well as chemokines including CCL17, CCL22, and CCL24. PAZ@Fe-MOF reprogramed the inhibitory immune microenvironment and curbed tumorigenicity by blocking the polarization of M2 phenotype macrophages. This platform offers a promising and new strategy for improving the cytotoxicity of PAZ against breast cancers. It provides a method to evaluate the immunological response of tumor cells to PAZ-mediated treatment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Immune microenvironment; M2-like macrophages; Metal-organic framework; Pazopanib.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Harris PA, Stafford JA. Discovery of Pazopanib: a Pan Vascular endothelial growth factor kinase inhibitor. 2009:57–77.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

