Anti-tumor effect of proteasome inhibitor on canine urothelial carcinoma
- PMID: 39034152
- PMCID: PMC11422692
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.23-0094
Anti-tumor effect of proteasome inhibitor on canine urothelial carcinoma
Abstract
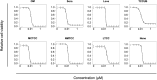
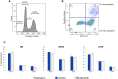
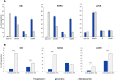
Canine urothelial carcinoma (cUC) is one of the most malignant tumors affecting dogs; however, its proliferative mechanism is yet to be fully elucidated. The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is an important metabolic pathway regulating protein degradation, and its dysfunction leads to apoptosis. We investigated the antitumor effect of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib, which blocks the UPS. Bortezomib inhibited cell growth in cUC cell lines by inducing apoptosis in vitro. These findings suggest the potential of bortezomib as a novel therapeutic drug for dogs with cUC.
Keywords: bortezomib; canine urothelial carcinoma; dog; proteasome inhibitor; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Araujo KPC, Bonuccelli G, Duarte CN, Gaiad TP, Moreira DF, Feder D, Belizario JE, Miglino MA, Lisanti MP, Ambrosio CE. 2013. Bortezomib (PS-341) treatment decreases inflammation and partially rescues the expression of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex in GRMD dogs. PLoS One 8: e61367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061367 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen FZ, Zhao XK. 2013. Ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and prostate cancer. Onkologie 36: 592–596. - PubMed

