Glutathione synthesis in the mouse liver supports lipid abundance through NRF2 repression
- PMID: 39034312
- PMCID: PMC11271484
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-50454-2
Glutathione synthesis in the mouse liver supports lipid abundance through NRF2 repression
Abstract
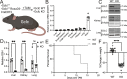
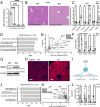
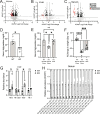
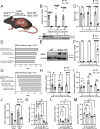
Cells rely on antioxidants to survive. The most abundant antioxidant is glutathione (GSH). The synthesis of GSH is non-redundantly controlled by the glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC). GSH imbalance is implicated in many diseases, but the requirement for GSH in adult tissues is unclear. To interrogate this, we have developed a series of in vivo models to induce Gclc deletion in adult animals. We find that GSH is essential to lipid abundance in vivo. GSH levels are highest in liver tissue, which is also a hub for lipid production. While the loss of GSH does not cause liver failure, it decreases lipogenic enzyme expression, circulating triglyceride levels, and fat stores. Mechanistically, we find that GSH promotes lipid abundance by repressing NRF2, a transcription factor induced by oxidative stress. These studies identify GSH as a fulcrum in the liver's balance of redox buffering and triglyceride production.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
I.S.H. reports financial support from Kojin Therapeutics. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
Glutathione supports lipid abundance in vivo.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 11:2023.02.10.524960. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.10.524960. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 21;15(1):6152. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50454-2. PMID: 36798186 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 CA230042/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA076292/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI181865/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 CA240533/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 210890/Z/18/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R24 AA022057/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA269813, R37CA230042,/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 AI150698/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI150698/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- R01 CA269813/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR078000/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA028859/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

