PEDF-34 attenuates neurological deficit and suppresses astrocyte-dependent neuroinflammation by modulating astrocyte polarization via 67LR/JNK/STAT1 signaling pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats
- PMID: 39034417
- PMCID: PMC11264993
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-024-03171-y
PEDF-34 attenuates neurological deficit and suppresses astrocyte-dependent neuroinflammation by modulating astrocyte polarization via 67LR/JNK/STAT1 signaling pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats
Abstract
Background: Reactive astrocytes participate in various pathophysiology after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), including neuroinflammation, glymphatic-lymphatic system dysfunction, brain edema, BBB disruption, and cell death. Astrocytes transform into two new reactive phenotypes with changed morphology, altered gene expression, and secretion profiles, termed detrimental A1 and beneficial A2. This study investigates the effect of 67LR activation by PEDF-34, a PEDF peptide, on neuroinflammation and astrocyte polarization after the experimental SAH.
Methods: A total of 318 male adult Sprague-Dawley rats were used in experiments in vivo, of which 272 rats were subjected to the endovascular perforation model of SAH and 46 rats underwent sham surgery. 67LR agonist (PEDF-34) was administrated intranasally 1 h after SAH. 67LR-specific inhibitor (NSC-47924) and STAT1 transcriptional activator (2-NP) were injected intracerebroventricularly 48 h before SAH. Short- and long-term neurological tests, brain water content, immunostaining, Nissl staining, western blot, and ELISA assay were performed. In experiments in vitro, primary astrocyte culture with hemoglobin (Hb) stimulation was used to mimic SAH. The expression of the PEDF-34/67LR signaling pathway and neuro-inflammatory cytokines were assessed using Western blot, ELISA, and immunohistochemistry assays both in vivo and in vitro.
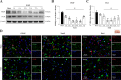
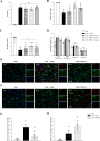
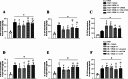
Results: Endogenous PEDF and 67LR expressions were significantly reduced at 6 h after SAH. 67LR was expressed in astrocytes and neurons. Intranasal administration of PEDF-34 significantly reduced brain water content, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and short-term and long-term neurological deficits after SAH. The ratio of p-JNK/JNK and p-STAT1/STAT1 and the expression of CFB and C3 (A1 astrocytes marker), significantly decreased after PEDF-34 treatment, along with fewer expression of TNF-α and IL-1β at 24 h after SAH. However, 2-NP (STAT1 transcriptional activator) and NSC-47924 (67LR inhibitor) reversed the protective effects of PEDF-34 in vivo and in vitro by promoting A1 astrocyte polarization with increased inflammatory cytokines.
Conclusion: PEDF-34 activated 67LR, attenuating neuroinflammation and inhibiting astrocyte A1 polarization partly via the JNK/STAT1 pathway, suggesting that PEDF-34 might be a potential treatment for SAH patients.
Keywords: Astrocyte polarization; Neuroinflammation; Non-integrin 67-kDa laminin receptor; Pigment epithelial-derived factor; Subarachnoid hemorrhage.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

