Exploring the Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in the Diagnosis and Management of Esthesioneuroblastomas: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 39036183
- PMCID: PMC11258942
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.62683
Exploring the Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in the Diagnosis and Management of Esthesioneuroblastomas: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
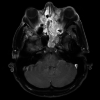
Esthesioneuroblastomas (ENBs) present unique diagnostic and therapeutic challenges due to their rare and complex clinical presentation. In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have emerged as promising tools in various medical specialties, revolutionizing diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning, and patient outcomes. However, their application in ENBs remains relatively unexplored. This comprehensive literature review aims to evaluate the current state of AI and ML technologies in ENB diagnosis, radiological and histopathological imaging, and treatment planning. By synthesizing existing evidence and identifying gaps in knowledge, this review aims to showcase the potential benefits, limitations, and future directions of integrating AI and ML into the multidisciplinary management of ENBs.
Keywords: artificial intelligence in radiology; artificial intelligence(ai); esthesioneuroblastoma and seizures; machine learning healthcare data; machine learning models.
Copyright © 2024, Patel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Comprehensive Review of Artificial Intelligence in Prostate Cancer Care: State-of-the-Art Diagnostic Tools and Future Outlook.Cureus. 2024 Aug 5;16(8):e66225. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66225. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39238711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Mental Healthcare: Current Trends and Future Directions - A Narrative Review for a Comprehensive Insight.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024 May 21;17:1339-1348. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S461562. eCollection 2024. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024. PMID: 38799612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revolutionizing Pulmonary Diagnostics: A Narrative Review of Artificial Intelligence Applications in Lung Imaging.Cureus. 2024 Apr 5;16(4):e57657. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57657. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38707160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Neuroendocrine Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 May 24;16(5):e61012. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61012. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38910787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence and Machine Learning approaches in sports: Concepts, applications, challenges, and future perspectives.Braz J Phys Ther. 2024 May-Jun;28(3):101083. doi: 10.1016/j.bjpt.2024.101083. Epub 2024 May 21. Braz J Phys Ther. 2024. PMID: 38838418 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Esthesioneuroblastoma: a comprehensive review of diagnosis, management, and current treatment options. Fiani B, Quadri SA, Cathel A, et al. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30862589/ World Neurosurg. 2019;126:194–211. - PubMed
-
- Diagnosis and management of esthesioneuroblastoma. Bradley PJ, Jones NS, Robertson I. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;11:112–118. - PubMed
-
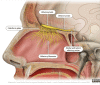
- Gaillard F. Olfactory nerve (illustration) [ May; 2024 ]. 2010. https://radiopaedia.org/cases/olfactory-nerve-illustration https://radiopaedia.org/cases/olfactory-nerve-illustration
-
- Esthesioneuroblastoma: a population-based analysis of survival and prognostic factors. Jethanamest D, Morris LG, Sikora AG, Kutler DI. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;133:276–280. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
