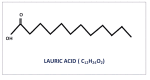Biomedical Applications of Lauric Acid: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 39036266
- PMCID: PMC11260118
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.62770
Biomedical Applications of Lauric Acid: A Narrative Review
Abstract
Lauric acid, a major component of coconut oil, has been studied for its various health benefits over the years. Lauric acid is a medium-chained fatty acid with several potential biomedical applications based on its antimicrobial action, capacity for drug delivery, tissue engineering scaffolds, and cleansing capabilities. Various studies are carried out in vitro and in vivo using experimental animals, such as rats, shedding light on the efficacy of lauric acid. The studies related to lauric acid were brought under one umbrella and emphasized the need for further research to explore the efficacy of lauric acid in human health. This review aims to scientifically assess the reported data and present a narrative review on lauric acid in medicine.
Keywords: anticancer agents; antihypertensive; antimicrobial; antitumour; biomedical; coconut oil; hypolipidemic; lauric acid; oral cavity cancer; oral diseases.
Copyright © 2024, M et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Coconut phytocompounds inhibits polyol pathway enzymes: implication in prevention of microvascular diabetic complications. Sheela DL, Nazeem PA, Narayanankutty A, et al. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017;127:20–24. - PubMed
-
- Lauric acid modulates cancer-associated microRNA expression and inhibits the growth of the cancer cell. Verma P, Ghosh A, Ray M, Sarkar S. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020;20:834–844. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources