Systematic exploration of therapeutic effects and key mechanisms of Panax ginseng using network-based approaches
- PMID: 39036729
- PMCID: PMC11258513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2024.01.005
Systematic exploration of therapeutic effects and key mechanisms of Panax ginseng using network-based approaches
Abstract
Background: Network pharmacology has emerged as a powerful tool to understand the therapeutic effects and mechanisms of natural products. However, there is a lack of comprehensive evaluations of network-based approaches for natural products on identifying therapeutic effects and key mechanisms.
Purpose: We systematically explore the capabilities of network-based approaches on natural products, using Panax ginseng as a case study. P. ginseng is a widely used herb with a variety of therapeutic benefits, but its active ingredients and mechanisms of action on chronic diseases are not yet fully understood.
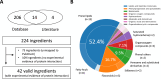
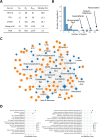
Methods: Our study compiled and constructed a network focusing on P. ginseng by collecting and integrating data on ingredients, protein targets, and known indications. We then evaluated the performance of different network-based methods for summarizing known and unknown disease associations. The predicted results were validated in the hepatic stellate cell model.
Results: We find that our multiscale interaction-based approach achieved an AUROC of 0.697 and an AUPR of 0.026, which outperforms other network-based approaches. As a case study, we further tested the ability of multiscale interactome-based approaches to identify active ingredients and their plausible mechanisms for breast cancer and liver cirrhosis. We also validated the beneficial effects of unreported and top-predicted ingredients, in cases of liver cirrhosis and gastrointestinal neoplasms.
Conclusion: our study provides a promising framework to systematically explore the therapeutic effects and key mechanisms of natural products, and highlights the potential of network-based approaches in natural product research.
Keywords: Network-based approach; Panax ginseng; Therapeutic effects.
© 2024 The Korean Society of Ginseng. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prediction of molecular mechanism of processed ginseng in the treatment of heart failure based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 8;102(49):e36576. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036576. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38065884 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the Regulatory Mechanism of Ginseng on the Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal Cancer based on Network Pharmacology and Bioinformatics Validation.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024;20(5):486-500. doi: 10.2174/1573409919666230607103721. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37287284
-
Systems-level mechanisms of action of Panax ginseng: a network pharmacological approach.J Ginseng Res. 2018 Jan;42(1):98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.09.001. Epub 2017 Oct 16. J Ginseng Res. 2018. PMID: 29348728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential mechanism of ginseng in the treatment of periodontitis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Apr 1;42(2):181-191. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2024.2023285. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38597078 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Analysis of common and characteristic actions of Panax ginseng and Panax notoginseng in wound healing based on network pharmacology and meta-analysis.J Ginseng Res. 2023 Jul;47(4):493-505. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.02.005. Epub 2023 Feb 22. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 37397412 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Herbal Remedies and Key Components for Major Depressive Disorder Through Biased Random Walk Analysis on a Multiscale Network.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 28;26(5):2162. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052162. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076790 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Candidate Polyphenols Beneficial for Oxidative Liver Injury through Multiscale Network Analysis.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 2;46(4):3081-3091. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040193. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666923 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Ginseng Bioactive Compound's Role in Hypertension Remedy: An In Silico Approach.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 28;18(5):648. doi: 10.3390/ph18050648. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430466 Free PMC article.
-
Ginseng and its functional components in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: therapeutic effects and multi-target pharmacological mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 9;16:1540255. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1540255. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40271056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network Medicine: A Potential Approach for Virtual Drug Screening.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 6;17(7):899. doi: 10.3390/ph17070899. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065749 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hopkins A.L. Network pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4(11):682–690. - PubMed
-
- Li S., Zhang B. Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: theory, methodology and application. Chin J Nat Med. 2013;11(2):110–120. - PubMed
-
- Li S., Zhang Z.Q., Wu L.J., Zhang X.G., Li Y.D., Wang Y.Y. Understanding ZHENG in traditional Chinese medicine in the context of neuro-endocrine-immune network. IET Syst Biol. 2007;1(1):51–60. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

