Monomeric and oligomeric amyloid-β cause distinct Alzheimer's disease pathophysiological characteristics in astrocytes in human glymphatics-on-chip models
- PMID: 39037244
- PMCID: PMC11302770
- DOI: 10.1039/d4lc00287c
Monomeric and oligomeric amyloid-β cause distinct Alzheimer's disease pathophysiological characteristics in astrocytes in human glymphatics-on-chip models
Abstract
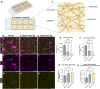
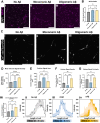
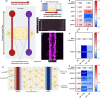
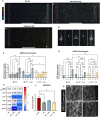
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is marked by the aggregation of extracellular amyloid-β (Aβ) and astrocyte dysfunction. For Aβ oligomers or aggregates to be formed, there must be Aβ monomers present; however, the roles of monomeric Aβ (mAβ) and oligomeric Aβ (oAβ) in astrocyte pathogenesis are poorly understood. We cultured astrocytes in a brain-mimicking three-dimensional (3D) extracellular matrix and revealed that both mAβ and oAβ caused astrocytic atrophy and hyper-reactivity, but showed distinct Ca2+ changes in astrocytes. This 3D culture evolved into a microfluidic glymphatics-on-chip model containing astrocytes and endothelial cells with the interstitial fluid (ISF). The glymphatics-on-chip model not only reproduced the astrocytic atrophy, hyper-reactivity, and Ca2+ changes induced by mAβ and oAβ, but recapitulated that the components of the dystrophin-associated complex (DAC) and aquaporin-4 (AQP4) were properly maintained by the ISF, and dysregulated by mAβ and oAβ. Collectively, mAβ and oAβ cause distinct AD pathophysiological characteristics in the astrocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

