Molecular mechanism of bitter taste receptor agonist-mediated relaxation of airway smooth muscle
- PMID: 39037554
- PMCID: PMC11299423
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202400452R
Molecular mechanism of bitter taste receptor agonist-mediated relaxation of airway smooth muscle
Abstract
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) belonging to the type 2 taste receptors (TAS2Rs) family are predominantly present in taste cells to allow the perception of bitter-tasting compounds. TAS2Rs have also been shown to be expressed in human airway smooth muscle (ASM), and TAS2R agonists relax ASM cells and bronchodilate airways despite elevating intracellular calcium. This calcium "paradox" (calcium mediates contraction by pro-contractile Gq-coupled GPCRs) and the mechanisms by which TAS2R agonists relax ASM remain poorly understood. To gain insight into pro-relaxant mechanisms effected by TAS2Rs, we employed an unbiased phosphoproteomic approach involving dual-mass spectrometry to determine differences in the phosphorylation of contractile-related proteins in ASM following the stimulation of cells with TAS2R agonists, histamine (an agonist of the Gq-coupled H1 histamine receptor) or isoproterenol (an agonist of the Gs-coupled β2-adrenoceptor) alone or in combination. Our study identified differential phosphorylation of proteins regulating contraction, including A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP)2, AKAP12, and RhoA guanine nucleotide exchange factor (ARHGEF)12. Subsequent signaling analyses revealed RhoA and the T853 residue on myosin light chain phosphatase (MYPT)1 as points of mechanistic divergence between TAS2R and Gs-coupled GPCR pathways. Unlike Gs-coupled receptor signaling, which inhibits histamine-induced myosin light chain (MLC)20 phosphorylation via protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent inhibition of intracellular calcium mobilization, HSP20 and ERK1/2 activity, TAS2Rs are shown to inhibit histamine-induced pMLC20 via inhibition of RhoA activity and MYPT1 phosphorylation at the T853 residue. These findings provide insight into the TAS2R signaling in ASM by defining a distinct signaling mechanism modulating inhibition of pMLC20 to relax contracted ASM.
Keywords: TAS2R; airway smooth muscle; asthma; chloroquine; rho a.
© 2024 The Author(s). The FASEB Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


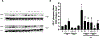



References
-
- Dolhnikoff M, da Silva LF, de Araujo BB, Gomes HA, Fernezlian S, Mulder A, Lindeman JH, and Mauad T (2009) The outer wall of small airways is a major site of remodeling in fatal asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123, 1090–1097, 1097 e1091 - PubMed
-
- Sears MR (2002) Adverse effects of beta-agonists. J Allergy Clin Immunol 110, S322–328 - PubMed
-
- Grove A, and Lipworth BJ (1995) Bronchodilator subsensitivity to salbutamol after twice daily salmeterol in asthmatic patients. Lancet 346, 201–206 - PubMed
-
- Wraight JM, Smith AD, Cowan JO, Flannery EM, Herbison GP, and Taylor DR (2004) Adverse effects of short-acting beta-agonists: potential impact when anti-inflammatory therapy is inadequate. Respirology 9, 215–221 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

