Sepsis Alert Systems, Mortality, and Adherence in Emergency Departments: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39037814
- PMCID: PMC11265133
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.22823
Sepsis Alert Systems, Mortality, and Adherence in Emergency Departments: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Importance: Early detection and management of sepsis are crucial for patient survival. Emergency departments (EDs) play a key role in sepsis management but face challenges in timely response due to high patient volumes. Sepsis alert systems are proposed to expedite diagnosis and treatment initiation per the Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines.
Objective: To review and analyze the association of sepsis alert systems in EDs with patient outcomes.
Data sources: A thorough search was conducted in PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library from January 1, 2004, to November 19, 2023.
Study selection: Studies that evaluated sepsis alert systems specifically designed for adult ED patients were evaluated. Inclusion criteria focused on peer-reviewed, full-text articles in English that reported on mortality, ICU admissions, hospital stay duration, and sepsis management adherence. Exclusion criteria included studies that lacked a control group or quantitative reports.
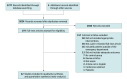
Data extraction and synthesis: The review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) reporting guideline. Two independent reviewers conducted the data extraction using a standardized form. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion. The data were synthesized using a random-effects model due to the expected heterogeneity among the included studies.
Main outcomes and measures: Key outcomes included mortality, intensive care unit admissions, hospital stay duration, and adherence to the sepsis bundle.
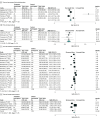
Results: Of 3281 initially identified studies, 22 (0.67%) met inclusion criteria, encompassing 19 580 patients. Sepsis alert systems were associated with reduced mortality risk (risk ratio [RR], 0.81; 95% CI, 0.71 to 0.91) and length of hospital stay (standardized mean difference [SMD], -0.15; 95% CI, -0.20 to -0.11). These systems were also associated with better adherence to sepsis bundle elements, notably in terms of shorter time to fluid administration (SMD, -0.42; 95% CI, -0.52 to -0.32), blood culture (SMD, -0.31; 95% CI, -0.40 to -0.21), antibiotic administration (SMD, -0.34; 95% CI, -0.39 to -0.29), and lactate measurement (SMD, -0.15; 95% CI, -0.22 to -0.08). Electronic alerts were particularly associated with reduced mortality (RR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.67 to 0.92) and adherence with blood culture guidelines (RR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.27).
Conclusions and relevance: These findings suggest that sepsis alert systems in EDs were associated with better patient outcomes along with better adherence to sepsis management protocols. These systems hold promise for enhancing ED responses to sepsis, potentially leading to better patient outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

