Pruritus Severity and Serum Phosphate in CKD: A Post Hoc Analysis of Difelikefalin Studies
- PMID: 39037824
- PMCID: PMC11441813
- DOI: 10.34067/KID.0000000000000520
Pruritus Severity and Serum Phosphate in CKD: A Post Hoc Analysis of Difelikefalin Studies
Abstract
Key Points:
No correlation was observed between pruritus severity and serum phosphate or response to placebo or difelikefalin in patients with CKD-associated pruritus undergoing hemodialysis.
Difelikefalin improved itch versus placebo irrespective of baseline serum phosphate.
Background: CKD-associated pruritus (CKD-aP) has historically been associated with elevated serum phosphate (sP). Difelikefalin is a novel antipruritic agent approved for the treatment of moderate-to-severe CKD-aP in adults undergoing hemodialysis. This post hoc analysis used data from phase 3 difelikefalin studies (KALM-1, KALM-2, and open-label Study 3105) to assess the role of sP in the pathogenesis of CKD-aP and whether difelikefalin ameliorates CKD-aP in patients with and without elevated sP.
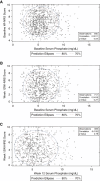
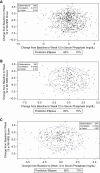
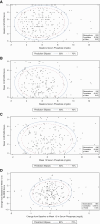
Methods: Patients with moderate-to-severe CKD-aP undergoing hemodialysis with baseline sP data were included in the analysis (KALM-1 and KALM-2, n=845; Study 3105, n=220). Assessments included correlation between 24-hour Worst Itching Intensity Numerical Rating Scale (WI-NRS) score and sP.
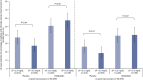
Results: In KALM-1 and KALM-2, baseline characteristics in the overall population were similar between patients with sP ≤5.5 and >5.5 mg/dl; no significant correlation was observed between WI-NRS and sP at baseline or in week 12. In patients receiving placebo, no correlation was observed between WI-NRS and sP at baseline or between their change from baseline to week 12 (all P < 0.05). Clinically meaningful (≥3-point) reductions from baseline to week 12 in WI-NRS scores were reported by more patients receiving placebo with baseline sP ≤5.5 mg/dl than >5.5 mg/dl (least squares mean 37.2% versus 27.4%; odds ratio [95% confidence interval], 0.63 [0.41 to 0.97]; P = 0.04). A greater proportion of patients treated with difelikefalin achieved a ≥3-point WI-NRS reduction from baseline to week 12 versus placebo and was similar between sP ≤5.5 and >5.5 mg/dl subgroups (least squares means 51.1% versus 57.6% [P = 0.20]). No significant relationships between sP and WI-NRS in patients receiving difelikefalin were identified in Study 3105 at any time point.
Conclusions: No correlation was observed between pruritus severity and sP or response to placebo or difelikefalin in patients with CKD-aP undergoing hemodialysis. Difelikefalin improved itch versus placebo irrespective of baseline sP.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03422653 NCT03636269 NCT03998163.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure forms, as provided by each author, are available with the online version of the article at
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

