Quality of life and tolerability of B-cell directed therapy of multiple sclerosis with ofatumumab in a patient-centered real-world observational study
- PMID: 39039273
- PMCID: PMC11377633
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-024-12581-0
Quality of life and tolerability of B-cell directed therapy of multiple sclerosis with ofatumumab in a patient-centered real-world observational study
Abstract
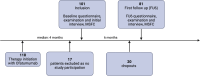
Introduction: Ofatumumab (Kesimpta®) is a subcutaneous CD20-targeting antibody approved in Germany in 2021 for the treatment of relapsing multiple sclerosis (RMS). After careful instruction, patients can administer the treatment themselves. We previously reported data of 101 patients (Klimas et al. in Nervenarzt 94:923-933, 2023). The objective of this longitudinal study is to explore the tolerability and acceptability of ofatumumab from a patient perspective over a follow up period of 6 months.
Methods: In this prospective observational real-world study, we report follow up data of 81 patients. We evaluated sociodemographic data, disease duration, duration and side effects of ofatumumab use, expanded disability status scale (EDSS), Beck Depression Inventory II (BDI-II), Short-Form 36 (SF-36), Fatigue Scale of Motor and Cognitive Functions (FSMC), and modified Multiple Sclerosis Functional Composite Test (MSFC). In addition, we asked for subjective treatment outcomes, such as impact on quality of life, walking distance, concentration, mood, medication adherence, fatigue and the subjective course of MS on a numerical rating scale (1 = very negative; 5 = very positive). Furthermore, treatment discontinuations were recorded.
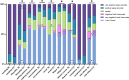
Results: The average duration of ofatumumab treatment was 10 months. In comparison to previous published data of our cohort, patients reported a significant increase in headache (10% up to 26%, p = 0.004) and limb pain (5% up to 26%, p < 0.001) as persistent side effects after the injections. More patients reported a very positive effect (p < 0.0001) on quality of life. 4 confirmed relapses occurred but no EDSS worsening, and no treatment discontinuations were documented during the observation period.
Discussion: As previously described, our prospective study indicates that patients have a good tolerability of ofatumumab, precisely because of the mild and few side effects at the first administration. However, the longer the observation period, the more headaches and limb pain occurred after the injections. Despite this, patients' subjective quality of life improved. There were no discontinuations during the follow-up period, with the limitation of a high loss to follow-up.
Keywords: Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody; B-cell depletion; Multiple sclerosis; Ofatumumab.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Anna-Sophia Karl: none. Rafael Klimas: received travel support from Takeda, Grifols, Ruhr-University Bochum and research support by Ruhr-University Bochum, and LFB Group France; none related to this manuscript. Melina Katsimpoura: none. Philip Lennart Poser: none. Simon Theile-Ochel: none. Melissa Sgodzai: none. Barbara Gisevius: none. Simon Faissner: has received speaker’s and/or scientific board honoraria and/or congress travel support from Academy2, AstraZeneca, Biogen, BMS, Celgene, Genesis Pharma, Hexal, Janssen, Merck, Neuraxpharm, Novartis and Roche and grant support from Ruhr-University Bochum, German Research Foundation (DFG), DMSG, DMSG North-Rhine-Westfalia, Stiftung für therapeutische Forschung, Lead Discovery Center GmbH and Novartis; none related to this manuscript. Anke Salmen: received speaker honoraria for activities with Bristol Myers Squibb, CSL Behring, Novartis, and Roche, and research support by the Baasch Medicus Foundation, the Medical Faculty of the University of Bern, the Swiss MS Society and the regional association of North Rhine-Westphalia of the German MS Society (DMSG Landesverband NRW). Ralf Gold: serves on scientific advisory boards for Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Biogen Idec, Bayer Schering Pharma, and Novartis; has received speaker honoraria from Biogen Idec, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Bayer Schering Pharma, and Novartis; serves as editor for Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Diseases and on the editorial boards of Experimental Neurology and the Journal of Neuroimmunology; and receives research support from Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Biogen Idec, Bayer Schering Pharma, Genzyme, Merck Serono, and Novartis, none related to this manuscript. Jeremias Motte: received speaker honoraria for activities with Alnylam, Biogen Idec, travel grants from Biogen Idec, Novartis AG, Teva, and Eisai GmbH; and his research is supported by Biogen Idec, Novartis AG, Kyverna Therapeutics Inc., GBS/CIDP Foundation International, Klaus TschiraFoundation, Hertie Foundation and Ruhr-University, Bochum, regional association of North Rhine-Westphalia of the German MS Society (DMSG Landesverband NRW); none related to this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- He A, Merkel B, Brown JWL, Zhovits Ryerson L, Kister I, Malpas CB, Sharmin S, Horakova D, Kubala Havrdova E, Spelman T, Izquierdo G, Eichau S et al (2020) Timing of high-efficacy therapy for multiple sclerosis: a retrospective observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol 19:307–316 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30067-3 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

