Dystrophin deficiency impairs cell junction formation during embryonic myogenesis from pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 39040067
- PMCID: PMC11261405
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110242
Dystrophin deficiency impairs cell junction formation during embryonic myogenesis from pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
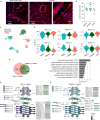
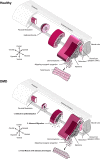
Mutations in the DMD gene lead to Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), a severe neuromuscular disorder affecting young boys as they acquire motor functions. DMD is typically diagnosed at 2-4 years of age, but the absence of dystrophin has negative impacts on skeletal muscles before overt symptoms appear in patients, which poses a serious challenge in current standards of care. Here, we investigated the consequences of dystrophin deficiency during skeletal muscle development. We used single-cell transcriptome profiling to characterize the myogenic trajectory of human pluripotent stem cells and showed that DMD cells bifurcate to an alternative branch when they reach the somite stage. Dystrophin deficiency was linked to marked dysregulations of cell junction proteins involved in the cell state transitions characteristic of embryonic somitogenesis. Altogether, this work demonstrates that in vitro, dystrophin deficiency has deleterious effects on cell-cell communication during myogenic development, which should be considered in future therapeutic strategies for DMD.
Keywords: biochemistry; biological sciences; cell biology; developmental biology; natural sciences; stem cells research.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


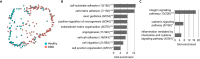


Update of
-
Dystrophin deficiency impairs cell junction formation during embryonic myogenesis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 8:2023.12.05.569919. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.05.569919. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: iScience. 2024 Jun 11;27(7):110242. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110242. PMID: 38106055 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bushby K., Finkel R., Birnkrant D.J., Case L.E., Clemens P.R., Cripe L., Kaul A., Kinnett K., McDonald C., Pandya S., et al. Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 1: diagnosis, and pharmacological and psychosocial management. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:77–93. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70271-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang C.H., Bonnemann C.G., Rutkowski A., Sejersen T., Bellini J., Battista V., Florence J.M., Schara U., Schuler P.M., Wahbi K., et al. Consensus statement on standard of care for congenital muscular dystrophies. J. Child Neurol. 2010;25:1559–1581. doi: 10.1177/0883073810381924. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

