Relationship between dynamic changes of microorganisms in Qupi and the quality formation of Fengxiangxing Huairang Daqu
- PMID: 39040905
- PMCID: PMC11260737
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1435765
Relationship between dynamic changes of microorganisms in Qupi and the quality formation of Fengxiangxing Huairang Daqu
Abstract
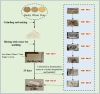
Introduction: Fengxiangxing Huairang Daqu (FHD) is one of the major types of Daqu in China. However, the relationship between the microbial community structure at different stages, the changes in the sensory characteristics, fermentation characteristics, volatiles, the most critical process point, and the quality formation of FHD is not clear.
Methods: Based on microscopic characterization, PacBio SMRT sequencing, and HS-SPME-GC-MS volatile metabolite analysis revealed the relationship between FHD quality formation and the dynamics of Qupi.
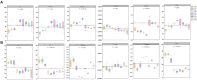
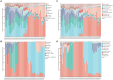
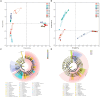
Results: The results showed that the 12th day of the culture was the most critical process point, highlighting the most significant differences in microbial community structure, sensory characteristics, fermentation characteristics, and flavor substances. Bacillus licheniformis (43.25%), Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula (35.05%), Thermoascus aurantiacus (76.51%), Aspergillus amstelodami (10.81%), and Saccharomycopsis fibuligera (8.88%) were the dominant species in FHD. S. fibuligera, A. amstelodami, and T. aurantiacus were associated with the snow-white color of the FHD epidermis, the yellow color of the interior, and the gray-white color, respectively. The abundance of T. aurantiacus, A. amstelodami, B. licheniformis, and S. rectivirgula was positively associated with the esterifying power and liquefying power of FHD. The abundance of T. aurantiacus and A. amstelodami was positively correlated with the saccharifying power of FHD. The abundance of S. fibuligera was positively related to the fermenting power of FHD. A total of 248 volatiles were detected in Qupi, mainly including alcohols, esters, aldehydes, and ketones. Of them, eleven volatiles had a significant effect on the flavor of Qupi, such as 1-butanol-3-methyl-, hydrazinecarboxamide, ethanol, phenylethyl alcohol, ethyl acetate, 2-octanone, 1-octen-3-ol, formic acid-hexyl ester, (E)-2-octen-1-ol, ethyl hexanoate, and 2(3H)-furanone-dihydro-5-pentyl-. The abundance of B. licheniformis, S. rectivirgula, T. aurantiacus, and S. fibuligera was positively correlated with the alcohols, aromatic compounds, and phenols in FHD. The abundance of S. fibuligera was positively correlated with the acids, esters, and hydrocarbons in FHD.
Discussion: These results indicate important theoretical basis and technical support for controllable adjustment of FHD microbial community structure, stable control of FHD quality, and precise, effective, and large-scale guidance of FHD production.
Keywords: Daqu quality formation; HS-SPME-GC-MS; PacBio sequencing; Qupi changes; fermentation characteristics; microorganisms; microscopic characterization; volatile metabolites.
Copyright © 2024 Cao, Lv, Chu, Xu, Jin, Zhang, Zhang, Zhang and Kang.
Conflict of interest statement
CJ, YoZ, and YuZ were employed by Shaanxi Xifeng Liquor Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Metabolic power, volatile compounds, and flavor marker formation mechanisms of three fungi isolated from Fengxiangxing Daqu.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 9;16:1593638. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1593638. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40415948 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic succession of microbial community in Nongxiangxing daqu and microbial roles involved in flavor formation.Food Res Int. 2022 Sep;159:111559. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111559. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35940779
-
Determining the changes in metabolites of Dendrobium officinale juice fermented with starter cultures containing Saccharomycopsis fibuligera FBKL2.8DCJS1 and Lactobacillus paracasei FBKL1.3028 through untargeted metabolomics.BMC Microbiol. 2023 Mar 14;23(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02807-y. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36918762 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Diversity and Volatile Flavor Compounds in Tibetan Flavor Daqu.Foods. 2023 Jan 9;12(2):324. doi: 10.3390/foods12020324. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36673416 Free PMC article.
-
Functional microorganisms in Baijiu Daqu: Research progress and fortification strategy for application.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jan 27;14:1119675. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1119675. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36778882 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of microbial communities with metabolites and enzyme activities in different colors of high-temperature Daqu.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Sep 12;41(9):324. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04562-w. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40936066
-
Metabolic power, volatile compounds, and flavor marker formation mechanisms of three fungi isolated from Fengxiangxing Daqu.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 9;16:1593638. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1593638. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40415948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cai H. Y., Liu W. J., Shen L. L., Wang J., Zhang H. P. (2022). Analysis of the structure of lactic acid Bacteria in Xinjiang fresh Mare Milk and koumiss using three generation sequencing technology. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 22, 291–300. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2022.02.031 - DOI
-
- Cai W. C., Xue Y. A., Wang Y. R., Wang W. P., Shu N., Zhao H. J., et al. (2021). The fungal communities and flavor profiles in different types of high-temperature Daqu as revealed by high-throughput sequencing and electronic senses. Front. Microbiol. 12:784651. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.784651, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deng J., Zheng J., Huang D., Huang Z. G., Ye G. B., Luo H. B. (2023). Characterization of physicochemical properties, volatile compounds and microbial community structure in four types of Daqu. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 184:115064. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2023.115064 - DOI
-
- Ding L., Zhao M. M., Zhao X. F., Chen G. Y., Jiang Q. T., Liu M., et al. (2022). Evaluation of the spatial distribution and dynamic succession of microbial community and quality properties during fermentation in Chinese medium-temperature Daqu. J. Food Process. Preserv. 46:e17272. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.17272 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

