The association of magnetic resonance imaging features with five molecular subtypes of breast cancer
- PMID: 39041054
- PMCID: PMC11261403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejro.2024.100585
The association of magnetic resonance imaging features with five molecular subtypes of breast cancer
Abstract
Objective: To identify the association of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) features with molecular subtypes of breast cancer (BC).
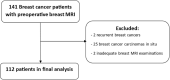
Materials and methods: A retrospective study was conducted on 112 invasive BC patients with preoperative breast MRI. The confirmed diagnosis and molecular subtypes of BC were based on the postoperative specimens. MRI features were collected by experienced radiologists. The association of MRI features of each subtype was compared to other molecular subtypes in univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses.
Results: The proportions of luminal A, luminal B HER2-negative, luminal B HER2-positive, HER2-enriched, and triple-negative BC were 14.3 %, 52.7 %, 12.5 %, 10.7 %, and 9.8 %, respectively. Luminal A was associated with hypo-isointensityon T2-weighted images (OR=6.214, 95 % CI: 1.163-33.215) and non-restricted diffusion on DWI-ADC (OR=6.694, 95 % CI: 1.172-38.235). Luminal B HER2-negative was related to the presence of mass (OR=7.245, 95 % CI: 1.760-29.889) and slow/medium initial enhancement pattern (OR=3.654, 95 % CI: 1.588-8.407). There were no associations between MRI features and luminal B HER2-positive. HER2-enriched tended to present as non-mass enhancement lesions (OR=20.498, 95 % CI: 3.145-133.584) with fast uptake in the initial postcontrast phase (OR=9.788, 95 % CI: 1.689-56.740), and distortion (OR=11.471, 95 % CI: 2.250-58.493). Triple-negative were associated with unifocal (OR=7.877, 95 % CI: 1.180-52.589), hyperintensityon T2-weighted images (OR=14.496, 95 % CI: 1.303-161.328), rim-enhanced lesions (OR=18.706, 95 % CI: 1.915-182.764), and surrounding tissue edema (OR=5.768, 95 % CI: 1.040-31.987).
Conclusion: Each molecular subtype of BC has distinct features on breast MRI. These characteristics can serve as an adjunct to immunohistochemistry in diagnosing molecular subtypes, particularly in cases, where traditional methods yield equivocal results.
Keywords: Breast cancer; MRI features; Molecular subtypes.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multiparametric MRI Features of Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Nov 23;58(12):1716. doi: 10.3390/medicina58121716. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36556918 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and diffusion-weighted MR imaging with prognostic factors and subtypes of breast cancers.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 5;12:942943. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.942943. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35992872 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of breast cancer subtypes based on quantitative assessment of intratumoral heterogeneity using dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.Eur Radiol. 2022 Feb;32(2):822-833. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08166-4. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34345946
-
Association between quantitative and qualitative image features of contrast-enhanced mammography and molecular subtypes of breast cancer.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022 Feb;12(2):1270-1280. doi: 10.21037/qims-21-589. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022. PMID: 35111622 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Phenotypes of Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes: A Systematic Review.Acad Radiol. 2022 Jan;29 Suppl 1:S89-S106. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2021.07.017. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Acad Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34481705
Cited by
-
Self-knowledge distillation for prediction of breast cancer molecular subtypes based on digital breast tomosynthesis.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2025 Jun 3. doi: 10.1007/s11517-025-03383-1. Online ahead of print. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2025. PMID: 40457128
-
Relationship of vitamin D receptor expression with hormone receptors and other clinicopathological features in primary breast carcinomas: A retrospective cross-sectional study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 29;104(35):e44222. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000044222. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40898467 Free PMC article.
-
Application of DCE-MRI radiomics and heterogeneity analysis in predicting luminal and non-luminal subtypes of breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 16;15:1523507. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1523507. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40308499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldhirsch A., Wood W.C., Coates A.S., et al. Strategies for subtypes--dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2011. Ann. Oncol. 2011;22(8):1736–1747. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr304. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous