Biomimetic Supramolecular Assembly with IGF-1C Delivery Ameliorates Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) by Restoring Intestinal Barrier Integrity
- PMID: 39041890
- PMCID: PMC11423171
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202403075
Biomimetic Supramolecular Assembly with IGF-1C Delivery Ameliorates Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) by Restoring Intestinal Barrier Integrity
Abstract
The management of dysfunctional intestinal epithelium by promoting mucosal healing and modulating the gut microbiota represents a novel therapeutic strategy for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). As a convenient and well-tolerated method of drug delivery, intrarectal administration may represent a viable alternative to oral administration for the treatment of IBD. Here, a biomimetic supramolecular assembly of hyaluronic acid (HA) and β-cyclodextrin (HA-β-CD) for the delivery of the C domain peptide of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1C), which gradually releases IGF-1C, is developed. It is identified that the supramolecular assembly of HA-β-CD enhances the stability and prolongs the release of IGF-1C. Furthermore, this biomimetic supramolecular assembly potently inhibits the inflammatory response, thereby restoring intestinal barrier integrity. Following HA-β-CD-IGF-1C administration, 16S rDNA sequencing reveals a significant increase in the abundance of the probiotic Akkermansia, suggesting enhanced intestinal microbiome homeostasis. In conclusion, the findings demonstrate the promise of the HA-based mimicking peptide delivery platform as a therapeutic approach for IBD. This biomimetic supramolecular assembly effectively ameliorates intestinal barrier function and intestinal microbiome homeostasis, suggesting its potential for treating IBD.
Keywords: C domain peptide of insulin‐like growth factor‐1 (IGF‐1C); inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); intestinal barrier integrity; microbiome homeostasis; supramolecular assembly.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

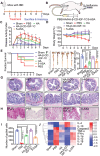
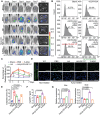


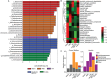

References
-
- Ananthakrishnan A. N., Bernstein C. N., Iliopoulos D., Macpherson A., Neurath M. F., Ali R. A. R., Vavricka S. R., Fiocchi C., Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 39. - PubMed
-
- Peterson L. W., Artis D., Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141. - PubMed
-
- a) Imberti B., Morigi M., Tomasoni S., Rota C., Corna D., Longaretti L., Rottoli D., Valsecchi F., Benigni A., Wang J., Abbate M., Zoja C., Remuzzi G., J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2921; - PubMed
- b) Xu J., Wang X., Chen J., Chen S., Li Z., Liu H., Bai Y., Zhi F., Theranostics 2020, 10, 12204. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U2004126/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82330066/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82270565/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81925021/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2017YFA0103200/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- NKYKD202203/Nankai University Eye Institute
- BKJ21J016/Research Project on Skin Injury & Repair
- TJYXZDXK-043A/Tianjin Key Medical Discipline (Specialty) Construction Project
- 22JCZXJC00170/Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Commission
- 21JCZDJC00070/Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
