Evaluation of Staining Propensity of Silver Diamine Fluoride With and Without Potassium Iodide in Children (Project Healthy Smiles): Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 39042887
- PMCID: PMC11303896
- DOI: 10.2196/51087
Evaluation of Staining Propensity of Silver Diamine Fluoride With and Without Potassium Iodide in Children (Project Healthy Smiles): Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Silver diamine fluoride (SDF) is becoming more widely recognized as a simple, cost-effective approach to minimize sensitivity and arrest caries. However, SDF results in caries that are stained black. Potassium iodide (KI) treatment with SDF may minimize or lessen the staining. However, the effectiveness of KI on staining has not been investigated. Studies demonstrating that potassium iodide reduces the black staining are still insufficient. This paper presents the study protocol for Healthy Smiles, a randomized controlled trial implemented to compare the staining propensity of SDF and SDF+KI.
Objective: This study, Healthy Smiles, aims to evaluate the staining propensity of SDF and SDF+KI using a Nix Mini color sensor among children aged 4 to 6 years. Another objective of the study is to evaluate the caries-arresting effect of SDF and SDF+KI in the treatment of carious primary teeth.
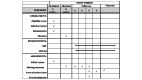
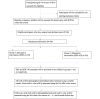
Methods: This study is a randomized controlled trial. A total of 60 children with caries that meet the criteria of the International Caries Detection and Assessment System (code 1 or above) will be randomly assigned to treatment groups, where group 1 will be treated with SDF and group 2 will be treated with SDF+KI. Discoloration of treated lesions will be assessed digitally using a Nix Mini color sensor. Participants will be followed up at 1, 3, and 6 months after treatment to digitally record the ∆L and ∆E values using the Nix Mini color sensor. Data will be analyzed using SPSS (version 28; IBM Corp). Independent sample t tests and the Mann-Whitney U test will be used to compare the 2 groups.
Results: Enrollment started in October 2023. It is estimated that the enrollment period will be 12 months. Data collection is planned to be completed in 2024.
Conclusions: The presented paper describes Happy Smiles, a project that provides an opportunity to address the aesthetic inconvenience of patients without compromising the effectiveness of the SDF treatment. The trial findings will contribute to the limited evidence base related to discoloration after SDF intervention to improve aesthetic appearances in child oral health. If the results from the trial are promising, it will lead to the development of a model for child oral health and pave the way for further research in child oral health.
International registered report identifier (irrid): PRR1-10.2196/51087.
Keywords: KI; SDF; child; dental; dental caries; dental esthetics; healthy smile; oral health; potassium iodide; silver diamine fluoride; staining; teeth; tooth discoloration; treatment.
©Praveena Navaneethan, Imran Pasha Mohammed, Rekha P Shenoy, Junaid Junaid, Supriya Amanna, Zeyad Alsughier, Shaul Hameed Kolarkodi. Originally published in JMIR Research Protocols (https://www.researchprotocols.org), 23.07.2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Mount G, Ngo H. Minimal intervention: a new concept for operative dentistry. Quintessence Int. 2000 Sep;31(8):527–33. - PubMed
-
- Nishino M, Yoshida S, Sobue S, Kato J, Nishida M. Effect of topically applied ammoniacal silver fluoride on dental caries in children. J Osaka Univ Dent Sch. 1969 Sep;9:149–55. - PubMed
-
- Crystal YO, Marghalani AA, Ureles SD, Wright JT, Sulyanto R, Divaris K, Fontana M, Graham L. Use of silver diamine fluoride for dental caries management in children and adolescents, including those with special health care needs. Pediatr Dent. 2017 Sep 15;39(5):135–145. - PubMed
-
- Zhao IS, Gao SS, Hiraishi N, Burrow MF, Duangthip D, Mei ML, Lo EC, Chu C. Mechanisms of silver diamine fluoride on arresting caries: a literature review. Int Dent J. 2018 Apr;68(2):67–76. doi: 10.1111/idj.12320. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/28542863 S0020-6539(20)31911-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

