Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections among Children before and during COVID-19 Pandemic, Taiwan, 2017-2023
- PMID: 39043456
- PMCID: PMC11286047
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3008.231596
Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections among Children before and during COVID-19 Pandemic, Taiwan, 2017-2023
Abstract
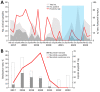
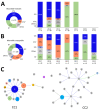
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections emerged during spring to summer yearly in Taiwan, but infections were few during the pandemic. M. pneumoniae macrolide resistance soared to 85.7% in 2020 but declined to 0% during 2022-2023. Continued molecular surveillance is necessary to monitor trends in macrolide-resistant M. pneumoniae.
Keywords: COVID-19; Mycoplasma pneumoniae; SARS; SARS-CoV-2; Taiwan; antimicrobial resistance; bacteria; coronavirus; coronavirus disease; macrolide resistance; molecular epidemiology; multilocus sequence typing; pneumonia; respiratory infections; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
References
-
- Meyer Sauteur PM, Beeton ML, Uldum SA, Bossuyt N, Vermeulen M, Loens K, et al. ; ESGMAC–MyCOVID Study Team. Mycoplasma pneumoniae detections before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: results of a global survey, 2017 to 2021. Euro Surveill. 2022;27:2100746. 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.19.2100746 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

