Unveiling the evolution of rotating black holes in loop quantum cosmology
- PMID: 39043863
- PMCID: PMC11266356
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-68000-x
Unveiling the evolution of rotating black holes in loop quantum cosmology
Abstract
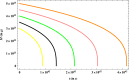
In this work, we aim to discuss about the evolution of rotating black holes (RBHs) within the context of loop quantum cosmology. Here, the main part of our research work focuses on the impacts of angular momentum based rotating parameter and accretion efficiency on the lifetime of RBHs. Our study reveals that accretion of dark energy would not significantly affect the evolution of RBHs, however higher value of rotating parameter could slightly delay the evaporation times of RBHs. Our analysis also depicts that the maximum value of rotating parameter for evolution of any RBH is , where is the formation mass of RBH. Moreover, from our calculation we found that the maximum mass of a presently existing supermassive black hole would be , if it undergoes rotation. Also from astrophysical constraint analysis, we found that there is a greater tendency for formation of black holes in loop quantum cosmology than standard model of cosmology.
Keywords: Dark energy; Loop quantum cosmology; Rotating black holes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Schwarzschild, K. On the gravitational field of a mass point according to Einstein’s theory. Sitz. Preuss. Akad. Wiss.1916, 189–196 (1916).
-
- Schwarzschild, K. On the gravitational field of a sphere of incompressible fluid according to Einstein’s theory. Sitz. Preuss. Akad. Wiss.1916, 424–434 (1916).
-
- Cooperstock, F. I. & de la Cruz, V. Sources for the reissner-nordström metric. Gen. Relativ. Gravit.9, 835–843 (1978). 10.1007/BF00760872 - DOI
-
- Bukhari, S. M. A. S., Pourhassan, B., Aounallah, H. & Wang, L. G. On the microstructure of higher-dimensional reissner-nordström black holes in quantum regime. Class. Quant. Grav.40, 225007 (2023). 10.1088/1361-6382/acffa0 - DOI
-
- Blagojević, M. & Cvetković, B. Entropy of reissner-nordström-like black holes. Phys. Lett. B824, 136815 (2022). 10.1016/j.physletb.2021.136815 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources