Stem cell collection and hematological recovery in the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi (FIL) MCL0208 clinical trial
- PMID: 39043871
- PMCID: PMC11266400
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-67906-w
Stem cell collection and hematological recovery in the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi (FIL) MCL0208 clinical trial
Abstract
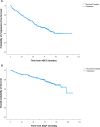
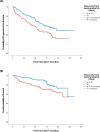
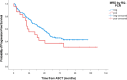
In the frontline high-dose phase 3 FIL-MCL0208 trial (NCT02354313), 8% of enrolled mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) patients could not be randomised to receive lenalidomide (LEN) maintenance vs observation after autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) due to inadequate hematological recovery and 52% of those who started LEN, needed a dose reduction due to toxicity. We therefore focused on the role played by CD34 + hematopoietic stem cells (PBSC) harvesting and reinfusion on toxicity and outcome. Overall, 90% (n = 245) of enrolled patients who underwent the first leukapheresis collected ≥ 4 × 106 PBSC/kg, 2.6% (n = 7) mobilized < 4 × 106 PBSC/kg and 7.7% (n = 21) failed the collection. Similar results were obtained for the planned second leukapheresis, with only one patient failing both attempts. Median count of reinfused PBSC was 5 × 106/kg and median time to recovery from neutropenia G4 was 10 days from ASCT. No impact of mobilizing subtype or number of reinfused PBSC on hematological recovery and LEN dose reduction was noted. At a median follow-up of 75 months from ASCT, PFS and OS of transplanted patients were 50% and 73%, respectively. A long lasting G4 neutropenia after ASCT (> 10 days) was associated with a worse outcome, both in terms of PFS and OS. In conclusion, although the harvesting procedures proved feasible for younger MCL patients, long-lasting cytopenia following ASCT remains a significant issue: this can hinder the administration of effective maintenance therapies, potentially increasing the relapse rate and negatively affecting survival outcomes.
Keywords: Autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT); Hematological recovery; Leukapheresis (LK); Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL); Peripheral blood stem cells (PBSC).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SF: Janssen, Recordati, Abbvie, Gilead, Beigene, Morphosys, Incyte, Clinigen, Italfarmaco, Astra Zeneca, Roche, Sandoz, Servier, Gentili; ML: AbbVie, Acerta, Amgen, GSKI, Gentili, Sandoz, Gilead/Kite, Novartis, Roche, Eusapharma, Takeda, Regeneron, Incyte, and Jazz, ADC Therapeutics, BeiGene, Celgene, Janssen; RT: Lilly, Janssen-Cilag; FC: Roche, Astra Zeneca, Servier; GG: Astra Zeneca, BeiGene, Incyte, Janssen, Lilly, Abbvie, Astra-Zeneca, Hikma, Janssen.
Figures

References
-
- Swerdlow, S.H. World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. https://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Who-Classification-O.... Accessed October 6, 2022.
-
- Dreyling, M. et al. Efficacy and safety of ibrutinib combined with standard first-line treatment or as substitute for autologous stem cell transplantation in younger patients with mantle cell lymphoma: Results from the randomized triangle trial by the European MCL network. Blood.140(Supplement 1), 1–3. 10.1182/blood-2022-163018 (2022). 10.1182/blood-2022-163018 - DOI
-
- Ladetto, M. et al. Lenalidomide maintenance after autologous haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in mantle cell lymphoma: Results of a Fondazione Italiana Linfomi (FIL) multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol.8(1), e34–e44. 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30358-6 (2021). 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30358-6 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

