Unlocking saponin biosynthesis in soapwort
- PMID: 39043959
- PMCID: PMC11782082
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-024-01681-7
Unlocking saponin biosynthesis in soapwort
Abstract
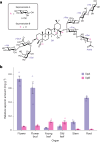
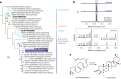
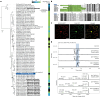
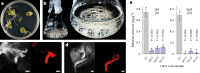
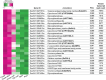
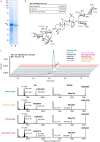
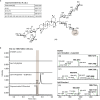
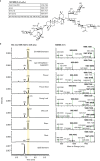
Soapwort (Saponaria officinalis) is a flowering plant from the Caryophyllaceae family with a long history of human use as a traditional source of soap. Its detergent properties are because of the production of polar compounds (saponins), of which the oleanane-based triterpenoid saponins, saponariosides A and B, are the major components. Soapwort saponins have anticancer properties and are also of interest as endosomal escape enhancers for targeted tumor therapies. Intriguingly, these saponins share common structural features with the vaccine adjuvant QS-21 and, thus, represent a potential alternative supply of saponin adjuvant precursors. Here, we sequence the S. officinalis genome and, through genome mining and combinatorial expression, identify 14 enzymes that complete the biosynthetic pathway to saponarioside B. These enzymes include a noncanonical cytosolic GH1 (glycoside hydrolase family 1) transglycosidase required for the addition of D-quinovose. Our results open avenues for accessing and engineering natural and new-to-nature pharmaceuticals, drug delivery agents and potential immunostimulants.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.J. and A.O. are inventors of a patent arising from this work (WO2024/003012, published), which relates to the biosynthesis of complex triterpenoid saponins and intermediates using the identified saponarioside pathway genes reported here. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Rogers, R. N. & Arnoldi, A. The Shroud of Turin: an amino-carbonyl reaction (Maillard reaction) may explain the image formation. Melanoidins4, 106–113 (2003).
-
- Johnson, L. A Manual of the Medical Botany of North America (William Wood & Company, 1884).
-
- Jia, Z. H., Koike, K. & Nikaido, T. Major triterpenoid saponins from Saponaria officinalis. J. Nat. Prod.61, 1368–1373 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Jia, Z., Koike, K. & Nikaido, T. Saponarioside C, the first α-d-galactose containing triterpenoid saponin, and five related compounds from Saponaria officinalis. J. Nat. Prod.62, 449–453 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Koike, K., Jia, Z. H. & Nikaido, T. New triterpenoid saponins and sapogenins from Saponaria officinalis. J. Nat. Prod.62, 1655–1659 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/V015176/1/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- NIF\R1\211270/Royal Society
- BB/X01097X/1/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- BB/T015063/1/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- John Innes Foundation (JIF)
- DE-AC02-05CH11231/DOE | Advanced Research Projects Agency - Energy (Advanced Research Projects Agency - Energy - U.S. Department of Energy)
- BB/W017857/1/RCUK | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- AT010593-01/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 AT010593/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

