An NAD+-dependent metabolic checkpoint regulates hematopoietic stem cell activation and aging
- PMID: 39044033
- PMCID: PMC11565225
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-024-00670-8
An NAD+-dependent metabolic checkpoint regulates hematopoietic stem cell activation and aging
Abstract
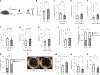
How hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) maintain metabolic homeostasis to support tissue repair and regeneration throughout the lifespan is elusive. Here, we show that CD38, an NAD+-dependent metabolic enzyme, promotes HSC proliferation by inducing mitochondrial Ca2+ influx and mitochondrial metabolism in young mice. Conversely, aberrant CD38 upregulation during aging is a driver of HSC deterioration in aged mice due to dysregulated NAD+ metabolism and compromised mitochondrial stress management. The mitochondrial calcium uniporter, a mediator of mitochondrial Ca2+ influx, also supports HSC proliferation in young mice yet drives HSC decline in aged mice. Pharmacological inactivation of CD38 reverses HSC aging and the pathophysiological changes of the aging hematopoietic system in aged mice. Together, our study highlights an NAD+ metabolic checkpoint that balances mitochondrial activation to support HSC proliferation and mitochondrial stress management to enhance HSC self-renewal throughout the lifespan, and links aberrant Ca2+ signaling to HSC aging.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
E.N.C. holds a patent on the use of CD38 inhibitors for metabolic diseases that is licensed by Elysium Health. E.N.C. is a consultant for TeneoBio, Calico, Mitobridge and Cytokinetics. E.N.C. is on the advisory board of Eolo Pharma. E.N.C. owns stocks in TeneoBio. Research in the Chini laboratory has been conducted in compliance with the Mayo Clinic conflict of interest policies. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


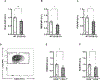
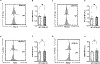

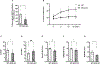
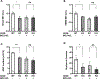
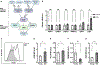

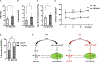
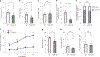


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG26094/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01DK117481/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 AG58812/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01AG063389/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01AG063404/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 CA233790/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA029124/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG058812/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR081788/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG026094/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG082105/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG063404/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK117481/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG063389/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG082105/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

