Effect of dexmedetomidine on somatosensory- and motor-evoked potentials in patients receiving craniotomy under propofol-sevoflurane combined anesthesia
- PMID: 39045089
- PMCID: PMC11263188
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1386049
Effect of dexmedetomidine on somatosensory- and motor-evoked potentials in patients receiving craniotomy under propofol-sevoflurane combined anesthesia
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Effect of dexmedetomidine on somatosensory- and motor evoked potentials in patients receiving craniotomy under propofol-sevoflurane combined anesthesia.Front Surg. 2024 Aug 28;11:1480011. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1480011. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2024. PMID: 39263583 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Dexmedetomidine is often used as an adjunct to total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA) for procedures requiring intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring (IONM). However, it has been reported that dexmedetomidine might mask the warning of a neurological deficit on intraoperative monitoring.
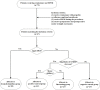
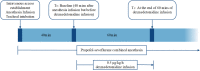
Methods: We reviewed the intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring data of 47 patients who underwent surgery and IONM from March 2019 to March 2021 at the Department of Neurosurgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University. Pre- and postoperative motor function scores were recorded and analyzed. Dexmedetomidine was administered intravenously at 0.5 μg/kg/h 40 min after anesthesia and discontinued after 1 h in the dexmedetomidine group.
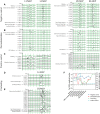
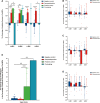
Results: We found that the amplitude of transcranial motor-evoked potentials (Tce-MEPs) was significantly lower in the dexmedetomidine group than in the negative control group (P < 0.0001). There was no statistically significant difference in the somatosensory-evoked potentials (SSEPs) amplitude or the Tce-MEPs or SSEPs latency. There was no significant decrease in postoperative motor function in the dexmedetomidine group compared with the preoperative group, suggesting that there is no evidence that dexmedetomidine affects patient prognosis. In addition, we noticed a synchronized bilateral decrease in the Tce-MEPs amplitude in the dexmedetomidine group and a mostly unilateral decrease on the side of the brain injury in the positive control group (P = 0.001).
Discussion: Although dexmedetomidine does not affect the prognosis of patients undergoing craniotomy, the potential risks and benefits of applying it as an adjunctive medication during craniotomy should be carefully evaluated. When dexmedetomidine is administered, Tce-MEPs should be monitored. When a decrease in the Tce-MEPs amplitude is detected, the cause of the decrease in the MEPs amplitude can be indirectly determined by whether the decrease is bilateral.
Keywords: dexmedetomidine; intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring; neurosurgery; prognosis; transcranial motor-evoked potentials.
© 2024 Yang, Zhang, Lin, Liu, Deng, Liang, Zhu, Qiao and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chang R, Reddy R, Coutinho D, Chang Y, Anetakis K, Crammond D, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of SSEP changes during lumbar spine surgery for predicting postoperative neurological deficit: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2021) 46:E1343–52. 10.1097/BRS.0000000000004099 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

