Head tracking using an optical soft tactile sensing surface
- PMID: 39045279
- PMCID: PMC11264287
- DOI: 10.3389/frobt.2024.1410858
Head tracking using an optical soft tactile sensing surface
Abstract
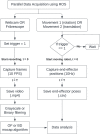
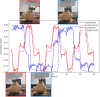
This research proposes a sensor for tracking the motion of a human head via optical tactile sensing. It implements the use of a fibrescope a non-metal alternative to a webcam. Previous works have included robotics grippers to mimic the sensory features of human skin, that used monochrome cameras and depth cameras. Tactile sensing has shown advantages in feedback-based interactions between robots and their environment. The methodology in this paper is utilised to track motion of objects in physical contact with these sensors to replace external camera based motion capture systems. Our immediate application is related to detection of human head motion during radiotherapy procedures. The motion was analysed in two degrees of freedom, respective to the tactile sensor (translational in z-axis, and rotational around y-axis), to produce repeatable and accurate results. The movements were stimulated by a robot arm, which also provided ground truth values from its end-effector. The fibrescope was implemented to ensure the device's compatibility with electromagnetic waves. The cameras and the ground truth values were time synchronised using robotics operating systems tools. Image processing methods were compared between grayscale and binary image sequences, followed by motion tracking estimation using deterministic approaches. These included Lukas-Kanade Optical Flow and Simple Blob Detection, by OpenCV. The results showed that the grayscale image processing along with the Lukas-Kanade algorithm for motion tracking can produce better tracking abilities, although further exploration to improve the accuracy is still required.
Keywords: head and neck; motion tracking; optical flow; radiotherapy; tactile sensing.
Copyright © 2024 Gandhi, Mihaylova and Dogramadzi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Alkkiomäki O., Kyrki V., Kälviäinen H., Liu Y., Handroos H. (2009). Complementing visual tracking of moving targets by fusion of tactile sensing. Robotics Aut. Syst. 57, 1129–1139. 10.1016/j.robot.2009.07.001 - DOI
-
- Ariz M., Villanueva A., Cabeza R. (2019). Robust and accurate 2d-tracking-based 3d positioning method: application to head pose estimation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 180, 13–22. 10.1016/j.cviu.2019.01.002 - DOI
-
- Bailer C., Taetz B., Stricker D. (2015). “Flow fields: dense correspondence fields for highly accurate large displacement optical flow estimation,” in Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV; ), 4015–4023. - PubMed
-
- Bansal M., Kumar M., Kumar M., Kumar K. (2021). An efficient technique for object recognition using shi-tomasi corner detection algorithm. Soft Comput. 25, 4423–4432. 10.1007/s00500-020-05453-y - DOI
-
- Bhogal R. K., Devendran V. (2023). “Motion estimating optical flow for action recognition: (farneback, horn schunck, lucas kanade and lucas-kanade derivative of Gaussian),” in 2023 International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things (IDCIoT) (IEEE), Bengaluru, India, 05-07 January 2023, 675–682. 10.1109/idciot56793.2023.10053515 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

