Genetic correlation and causal relationship between sleep and myopia: a mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 39045316
- PMCID: PMC11263174
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1378802
Genetic correlation and causal relationship between sleep and myopia: a mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the genetic correlation and causal links between sleep traits (including sleep duration, chronotype, and insomnia) and myopia.
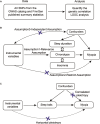
Methods: Summary data on three sleep traits (sleep duration, chronotype and insomnia) and myopia from FinnGen (n = 214,211) and UK Biobank (n = 460,536) were analyzed using linkage disequilibrium score regression (LD Score), univariable and multivariable mendelian randomization (MR) experiments and Causal Analysis Using Summary Effect (CAUSE) estimation.
Results: LD Score regression detected candidate genetic correlation between sleep traits and myopia, such as sleep duration, chronotype (Genetic Correlation Z-score >10.00, h2_observed_p < 0.005, Lambda GC > 1.05, p > 0.05). Univariable MR analyses indicated that increased sleep duration has a promotional effect on the occurrence of myopia (p = 0.046 < 0.05, P_FDR = 0.138 < 0.2, OR = 2.872, 95% CI: 1.018-8.101). However, after accounting for potential confounding factors, multivariable MR and CAUSE analysis did not provide evidence for a causal effect of the three sleep traits on myopia.
Conclusion: There may be a potential genetic correlation between sleep duration, chronotype and myopia. However, neither of sleep duration, chronotype or insomnia had causal effect on myopia.
Keywords: causal analysis using summary effect; chronotype; insomnia; mendelian randomization; myopia; sleep duration.
Copyright © 2024 Zhu, Tian, Zhou and Qin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

