Therapeutic efficacy of pyronaridine-artesunate (Pyramax) in treating Plasmodium vivax malaria in the central highlands of Vietnam
- PMID: 39046237
- PMCID: PMC11373200
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00044-24
Therapeutic efficacy of pyronaridine-artesunate (Pyramax) in treating Plasmodium vivax malaria in the central highlands of Vietnam
Abstract
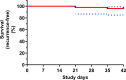
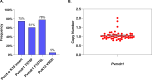
The emergence and spread of chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium vivax have necessitated the assessment of alternative blood schizonticidal drugs. In Vietnam, chloroquine-resistant P. vivax malaria has been reported. In an open-label, single-arm trial, the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of pyronaridine-artesunate (Pyramax, PA) was evaluated in Dak Nong province, Vietnam. A 3-day course of PA was administered to adults and children (≥20 kg) infected with P. vivax. Patients also received primaquine (0.25 mg/kg daily for 14 days). PA was well tolerated with transient asymptomatic increases in liver transaminases. The per-protocol proportion of patients with day 42 PCR-unadjusted adequate clinical and parasitological response was 96.0% (95% CI, 84.9%-99.0%, n = 48/50). The median parasite clearance time was 12 h (range, 12-36 h), with a median fever clearance time of 24 h (range, 12-60 h). Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) as potential genetic markers of reduced drug susceptibility were analyzed in three putative drug resistance markers, Pvcrt-o, Pvmdr1, and PvK12. Insertion at position K10 of the Pvcrt-o gene was found in 74.6% (44/59) of isolates. Pvmdr1 SNPs at Y976F and F1076L were present in 61% (36/59) and 78% (46/59), respectively. Amplification of Pvmdr1 gene (two copies) was found in 5.1% (3/59) of parasite samples. Only 5.1% (3/59) of isolates had mutation 552I of the PvK12 gene. Overall, PA rapidly cleared P. vivax blood asexual stages and was highly efficacious in treating vivax malaria, with no evidence of artemisinin resistance found. PA provides an alternative to chloroquine treatment for vivax malaria in Vietnam.
Clinical trials: This study is registered with the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry as ACTRN12618001429246.
Keywords: Plasmodium vivax; Pyramax; Vietnam; antimalarial drug resistance; molecular markers; pyronaridine-artesunate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lacerda MVG, Mourão MPG, Alexandre MAA, Siqueira AM, Magalhães BML, Martinez-Espinosa FE, Filho FSS, Brasil P, Ventura AMRS, Tada MS, Couto VSCD, Silva AR, Silva RSU, Alecrim MGC. 2012. Understanding the clinical spectrum of complicated Plasmodium vivax malaria: a systematic review on the contributions of the Brazilian literature. Malar J 11:12. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-11-12 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Commons RJ, Simpson JA, Thriemer K, Hossain MS, Douglas NM, Humphreys GS, Sibley CH, Guerin PJ, Price RN. 2019. Risk of Plasmodium vivax parasitaemia after Plasmodium falciparum infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 19:91–101. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30596-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO . 2023. World malaria report 2023. Geneva
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

