Spiramycin-loaded maltodextrin nanoparticles as a promising treatment of toxoplasmosis on murine model
- PMID: 39046555
- PMCID: PMC11269460
- DOI: 10.1007/s00436-024-08280-4
Spiramycin-loaded maltodextrin nanoparticles as a promising treatment of toxoplasmosis on murine model
Abstract
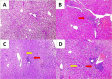
Despite being the initial choice for treating toxoplasmosis, sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine have limited effectiveness in eliminating the infection and were linked to a variety of adverse effects. Therefore, the search for new effective therapeutic strategies against toxoplasmosis is still required. The current work is the first research to assess the efficacy of spiramycin-loaded maltodextrin nanoparticles (SPM-loaded MNPs) as a novel alternative drug therapy against toxoplasmosis in a murine model. Fifty laboratory-bred Swiss albino mice were divided into five groups: normal control group (GI, n = 10), positive control group (GII, n = 10), orally treated with spiramycin (SPM) alone (GIII, n = 10), intranasal treated with SPM-loaded MNPs (GIV, n = 10), and orally treated with SPM-loaded MNPs (GV, n = 10). Cysts of Toxoplasma gondii ME-49 strain were used to infect the mice. Tested drugs were administered 2 months after the infection. Drug efficacy was assessed by counting brain cysts, histopathological examination, and measures of serum CD19 by flow cytometer. The orally treated group with SPM-loaded MNPs (GV) showed a marked reduction of brain cyst count (88.7%), histopathological improvement changes, and an increasing mean level of CD19 (80.2%) with significant differences. SPM-loaded MNPs showed potent therapeutic effects against chronic toxoplasmosis. Further research should be conducted to assess it in the treatment of human toxoplasmosis, especially during pregnancy.
Keywords: Maltodextrin nanoparticles; Spiramycin; Toxoplasmosis; Treatment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Abdallah K, Saleh M, Kishk S, Barakat A, Ali B, elkholy A (2022) A new approach in treatment of chronic murine models of toxoplasmosis using nitrofurantoin antibiotic. ZUMJ 1169–1175. 10.21608/zumj.2022.112316.2440
-
- Allam AF, Hagras NA, Farag HF, Osman MM, Shalaby TI, Kazem AH, Shehab AY, Mogahed NM (2022) Remarkable histopathological improvement of experimental toxoplasmosis after receiving spiramycin-chitosan nanoparticles formulation. J Parasit Dis 46(1):166–177. 10.1007/s12639-021-01431-9 10.1007/s12639-021-01431-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheraghipour K, Masoori L, Ezzatkhah F, Salimikia I, Amiri S, Makenali AS, Taherpour F, Mahmoudvand H (2020) Effect of chitosan on Toxoplasma gondii infection: a systematic review. Parasite Epidemiol Control 21(11):e00189. 10.1016/j.parepi.2020.e0018910.1016/j.parepi.2020.e00189 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

