Alterations of ceramide synthesis induce PD-L1 internalization and signaling to regulate tumor metastasis and immunotherapy response
- PMID: 39046874
- PMCID: PMC11404065
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114532
Alterations of ceramide synthesis induce PD-L1 internalization and signaling to regulate tumor metastasis and immunotherapy response
Abstract
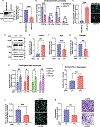
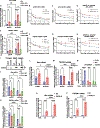
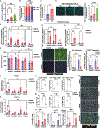
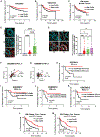
Programmed death ligand 1, PD-L1 (CD274), facilitates immune evasion and exerts pro-survival functions in cancer cells. Here, we report a mechanism whereby internalization of PD-L1 in response to alterations of bioactive lipid/ceramide metabolism by ceramide synthase 4 (CerS4) induces sonic hedgehog (Shh) and transforming growth factor β receptor signaling to enhance tumor metastasis in triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs), exhibiting immunotherapy resistance. Mechanistically, data showed that internalized PD-L1 interacts with an RNA-binding protein, caprin-1, to stabilize Shh/TGFBR1/Wnt mRNAs to induce β-catenin signaling and TNBC growth/metastasis, consistent with increased infiltration of FoxP3+ regulatory T cells and resistance to immunotherapy. While mammary tumors developed in MMTV-PyMT/CerS4-/- were highly metastatic, targeting the Shh/PD-L1 axis using sonidegib and anti-PD-L1 antibody vastly decreased tumor growth and metastasis, consistent with the inhibition of PD-L1 internalization and Shh/Wnt signaling, restoring anti-tumor immune response. These data, validated in clinical samples and databases, provide a mechanism-based therapeutic strategy to improve immunotherapy responses in metastatic TNBCs.
Keywords: CP: Cancer; CP: Metabolism; CerS4; PD-L1; ceramide; immunotherapy; metastasis; sonic hedgehog; sphingolipid.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Xu J, Acharya S, Sahin O, Zhang Q, Saito Y, Yao J, Wang H, Li P, Zhang L, Lowery FJ, et al. (2015). 14–3-3ζ turns TGF-β’s function from tumor suppressor to metastasis promoter in breast cancer by contextual changes of Smad partners from p53 to Gli2. Cancer Cell 27, 177–192. 10.1016/j.ccell.2014.11.025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

