THREE-DIMENSIONAL RETINAL DISPLACEMENT BEFORE AND AFTER MACULAR PUCKER SURGERY
- PMID: 39047126
- PMCID: PMC11288389
- DOI: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000004125
THREE-DIMENSIONAL RETINAL DISPLACEMENT BEFORE AND AFTER MACULAR PUCKER SURGERY
Abstract
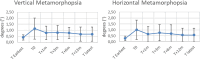
Purpose: To measure the coronal and sagittal retinal displacement before and after surgery for epiretinal membranes in InfraRed horizontal foveal sections and optical coherence tomography scans and describe displacement tridimensionality, vision loss, and metamorphopsia.
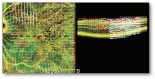
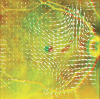
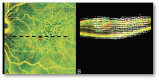
Methods: Retrospective series with greater than 6-month average follow-up before and after surgery. The record included best-corrected visual acuity, optical coherence tomography, M-charts, and InfraRed retinography. Overall, pre- and postoperative coronal and sagittal retinal displacement across the entire field, concentric circles at 0.5-, 1.5-, and 4.5-mm radii, and the central horizontal and vertical meridian were calculated as the optical flow of consecutive images.
Results: This study comprised 10 patients (4 men, 6 women), with 22.7 ± 25.2 months follow-up before surgery and 16.2 ± 7.3 months after. Best-corrected visual acuity reduced before surgery (0.15 ± 0.67 logarithm of minimum angle of resolution to 0.38 ± 0.85 logarithm of minimum angle of resolution; P < 0.05) and increased afterward (0.086 ± 0.61 logarithm of minimum angle of resolution; P = 0.003). Preoperative coronal displacement was 30.1 ± 29.1 µm versus 67.0 ± 23.4 µm after (P = 0.002). Sagittal retinal displacement was 140.9 ± 84.6 µm before surgery, 339.7 ± 172.5 µm after (P = 0.017), and 357.6 ± 320.8 µm across the entire follow-up. Preoperative best-corrected visual acuity decreases correlated with the foveal coronal displacement. Vertical metamorphopsia correlated with the average coronal displacement within a 4.5-mm radius. Pre- and postoperative sagittal displacement correlated with horizontal metamorphopsia (P = 0.006 and P = 0.026). Postoperative sagittal displacement correlated with postoperative best-corrected visual acuity (P = 0.026) and foveal thickness (P = 0.009).
Conclusion: This study confirms that postoperative displacement is greater than preoperative and that sagittal displacement is greater than coronal and correlates with best-corrected visual acuity and metamorphopsia changes.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Opthalmic Communications Society, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any financial/conflicting interests to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Simunovic MP. Metamorphopsia and its quantification. Retina 2015;35:1285–1291. - PubMed
-
- Romano MR, Cennamo G, Amoroso F, et al. . Intraretinal changes in the presence of epiretinal traction. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2017;255:31–38. - PubMed
-
- Chang S, Gregory-Roberts EM, Park S, et al. . Double peeling during vitrectomy for macular pucker: the Charles L. Schepens Lecture. JAMA Ophthalmol 2013;131:525–530. - PubMed
-
- Scarinci F, Querzoli G, Cosimi P, et al. . Retinal tectonics after macular pucker surgery: thickness changes and en face displacement recovery. Retina 2024;44:102–110. - PubMed
-
- Ichikawa Y, Imamura Y, Ishida M. Inner nuclear layer thickness, a biomarker of metamorphopsia in epiretinal membrane, correlates with tangential retinal displacement. Am J Ophthalmol 2018;193:20–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

