Long-term outcomes of patients affected by Guillain-Barré syndrome in Colombia after the Zika virus epidemic
- PMID: 39047509
- PMCID: PMC11338696
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jns.2024.123140
Long-term outcomes of patients affected by Guillain-Barré syndrome in Colombia after the Zika virus epidemic
Abstract
Background: Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) can lead to significant functional impairments, yet little is understood about the recovery phase and long-term consequences for patients in low- and medium-income countries.
Objective: To evaluate the functional status and identify factors influencing outcomes among patients with GBS in Colombia.
Methods: Telephone interviews were conducted with GBS patients enrolled in the Neuroviruses Emerging in the Americas Study between 2016 and 2020. The investigation encompassed access to health services and functional status assessments, utilizing the modified Rankin Scale (mRS), GBS Disability Score (GDS), Barthel Index (BI), and International Classification of Functioning (ICF). Univariate analysis, principal component analysis, linear discriminant analysis, and linear regression were employed to explore factors influencing functional status.
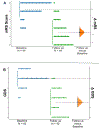
Results: Forty-five patients (mean age = 50[±22] years) with a median time from diagnosis of 28 months (IQR = 9-34) were included. Notably, 22% and 16% of patients did not receive rehabilitation services during the acute episode and post-discharge, respectively. Most patients demonstrated independence in basic daily activities (median BI = 100, IQR = 77.5-100), improvement in disability as the median mRS at follow-up was lower than at onset (1 [IQR = 0-3] vs. 4.5 [IQR = 4-5], p < 0.001), and most were able to walk without assistance (median GDS = 2, IQR = 0-2). A shorter period from disease onset to interview was associated with worse mRS (p = 0.015) and ICF (p = 0.019). Negative outcomes on GDS and ICF were linked to low socioeconomic status, ICF to the severity of weakness at onset, and BI to an older age.
Conclusions: This study underscores that the functional recovery of GBS patients in Colombia is influenced not only by the natural course of the disease but also by socioeconomic factors, emphasizing the crucial role of social determinants of health.
Keywords: Activities of daily living; Guillain-Barré syndrome; Low- and middle-income countries; Neurological rehabilitation; Peripheral nerves; Polyneuropathies; Quality of life; Recovery of function.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest Declarations of interest: none.
Figures
References
-
- Goodfellow JA, Willison HJ. Guillain-Barré syndrome: a century of progress. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12(12):723–731. - PubMed
-
- Soysal A, Aysal F, Caliskan B, Dogan Ak P, Mutluay B, Sakalli N, et al. Clinico-electrophysiological findings and prognosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome−-10 years’ experience. Acta Neurol Scand. 2011. Mar;123(3):181–6. - PubMed
-
- van den Berg B, Storm EF, Garssen MJP, Blomkwist-Markens PH, Jacobs BC. Clinical outcome of Guillain-Barré syndrome after prolonged mechanical ventilation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018. Sep;89(9):949–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

