SomaLogic proteomics reveals new biomarkers and provides mechanistic, clinical insights into Acetyl coA Carboxylase (ACC) inhibition in Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
- PMID: 39048608
- PMCID: PMC11269579
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-67843-8
SomaLogic proteomics reveals new biomarkers and provides mechanistic, clinical insights into Acetyl coA Carboxylase (ACC) inhibition in Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
Abstract
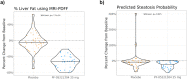
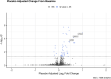
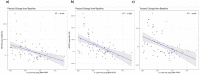
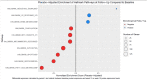
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) are major metabolic diseases with increasing global prevalence and no approved therapies. There is a mounting need to develop biomarkers of diagnosis, prognosis and treatment response that can effectively replace current requirements for liver biopsies, which are invasive, error-prone and expensive. We performed SomaLogic serum proteome profiling with baseline (n = 231) and on-treatment (n = 72, Weeks 12 and 16, Placebo and 25 mg PF-05221304) samples from a Phase 2a trial (NCT03248882) with Clesacostat (PF-05221304), an acetyl coA carboxylase inhibitor (ACCi) in patients with NAFLD/NASH. SomaSignal NASH probability scores and expression data for 7000+ analytes were analyzed to identify potential biomarkers associated with baseline clinical measures of NAFLD/NASH [Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Proton Density Fat Fraction (MRI-PDFF), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST)] as well as biomarkers of treatment response to ACCi. SomaSignal NASH probability scores identified biopsy-proven/clinically defined NIT-based (Presumed) NASH classification of the cohort with > 70% agreement. Clesacostat-induced reduction in steatosis probability scores aligned with observed clinical reduction in hepatic steatosis based on MRI-PDFF. We identify a set of 69 analytes that robustly correlate with clinical measures of hepatic inflammation and steatosis (MRI-PDFF, ALT and AST), 27 of which were significantly reversed with ACC inhibition. Clesacostat treatment dramatically upregulated Wnt5a protein and Apolipoproteins C3 and E, with drug-induced changes significantly correlating to changes on MRI-PDFF. Our data demonstrate the utility of SomaLogic- analyte panel for diagnosis and treatment response in NAFLD/NASH and provide potential new mechanistic insights into liver steatosis reduction, inflammation and serum triglyceride elevation with ACC inhibition. (Clinical Trial Identifier: NCT03248882).
Keywords: Acetyl CoA Carboxylase; Biomarkers; Liver fibrosis; NAFLD/NASH; SomaLogic proteomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors were Pfizer employees at the time of the work and shareholders of Pfizer Inc.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

