Neurocognitive profiles of 22q11.2 and 16p11.2 deletions and duplications
- PMID: 39048645
- PMCID: PMC11746132
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-024-02661-y
Neurocognitive profiles of 22q11.2 and 16p11.2 deletions and duplications
Abstract
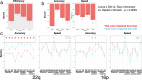
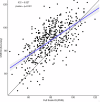
Rare recurrent copy number variants (CNVs) at chromosomal loci 22q11.2 and 16p11.2 are genetic disorders with lifespan risk for neuropsychiatric disorders. Microdeletions and duplications are associated with neurocognitive deficits, yet few studies compared these groups using the same measures to address confounding measurement differences. We report a prospective international collaboration applying the same computerized neurocognitive assessment, the Penn Computerized Neurocognitive Battery (CNB), administered in a multi-site study on rare genomic disorders: 22q11.2 deletions (n = 492); 22q11.2 duplications (n = 106); 16p11.2 deletion (n = 117); and 16p11.2 duplications (n = 46). Domains examined include executive functions, episodic memory, complex cognition, social cognition, and psychomotor speed. Accuracy and speed for each domain were included as dependent measures in a mixed-model repeated measures analysis. Locus (22q11.2, 16p11.2) and Copy number (deletion/duplication) were grouping factors and Measure (accuracy, speed) and neurocognitive domain were repeated measures factors, with Sex and Site as covariates. We also examined correlation with IQ. We found a significant Locus × Copy number × Domain × Measure interaction (p = 0.0004). 22q11.2 deletions were associated with greater performance accuracy deficits than 22q11.2 duplications, while 16p11.2 duplications were associated with greater specific deficits than 16p11.2 deletions. Duplications at both loci were associated with reduced speed compared to deletions. Performance profiles differed among the groups with particularly poor memory performance of the 22q11.2 deletion group while the 16p11.2 duplication group had greatest deficits in complex cognition. Average accuracy on the CNB was moderately correlated with Full Scale IQ. Deletions and duplications of 22q11.2 and 16p11.2 have differential effects on accuracy and speed of neurocognition indicating locus specificity of performance profiles. These profile differences can help inform mechanistic substrates to heterogeneity in presentation and outcome, and can only be established in large-scale international consortia using the same neurocognitive assessment. Future studies could aim to link performance profiles to clinical features and brain function.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JASV has served as a consultant for NoBias Therapeutics Inc. Other authors report no disclosures. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The research involving human subjects, human material, or human data was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) of the participating institutions approved all study procedures and the protocol was run under the oversight of the University of Pennsylvania Institutional Review Board (IRB # 832678). Informed consent/assent was obtained from each participant or accompanying parent or guardian according to local country guidelines.
Figures

Update of
-
Neurocognitive Profiles of 22q11.2 and 16p11.2 Deletions and Duplications.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 29:rs.3.rs-3393845. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3393845/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Feb;30(2):379-387. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02661-y. PMID: 38234766 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- U01 MH119736/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119758/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119738/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH117014/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH085953/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- MH119737/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- U01 MH119741/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119690/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH119741/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- MH119736/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- MH119759/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- U01 MH119746/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH116473/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085953/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119739/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH119740/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- U01 MH119740/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH119738/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- U01 MH119737/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH117014/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- R37 MH085953/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119759/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States

