Single-cell multi-omic and spatial profiling of human kidneys implicates the fibrotic microenvironment in kidney disease progression
- PMID: 39048792
- PMCID: PMC11592391
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01802-x
Single-cell multi-omic and spatial profiling of human kidneys implicates the fibrotic microenvironment in kidney disease progression
Abstract
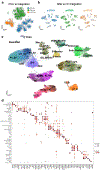
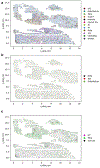
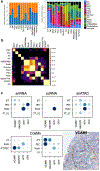
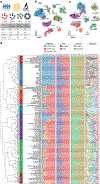
Kidneys are intricate three-dimensional structures in the body, yet the spatial and molecular principles of kidney health and disease remain inadequately understood. We generated high-quality datasets for 81 samples, including single-cell, single-nuclear, spot-level (Visium) and single-cell resolution (CosMx) spatial-RNA expression and single-nuclear open chromatin, capturing cells from healthy, diabetic and hypertensive diseased human kidneys. Combining these data, we identify cell types and map them to their locations within the tissue. Unbiased deconvolution of the spatial data identifies the following four distinct microenvironments: glomerular, immune, tubule and fibrotic. We describe the complex organization of microenvironments in health and disease and find that the fibrotic microenvironment is able to molecularly classify human kidneys and offers an improved prognosis compared to traditional histopathology. We provide a comprehensive spatially resolved molecular roadmap of the human kidney and the fibrotic process, demonstrating the clinical utility of spatial transcriptomics.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
K.D. and L.M. are employees of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. G.P., T.B., E.H. and L.S.B. are employees of GSK. S.P., C.M.B. and P.G. are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim. A.K. is an employee of Novo Nordisk. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












References
-
- Gueutin V, Deray G & Isnard-Bagnis C Renal physiology. Bull. Cancer 99, 237–249 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- DK105821/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- DK076077/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 DK087635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK123594/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01HG013185/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- P50 DK114786/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50DK114786/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 DK132630/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK019525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK019525/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 DK105821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK050306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK132630/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- U01DK134995/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- DK087635/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- U01DK112217/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 DK076077/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

