Human TMEFF1 is a restriction factor for herpes simplex virus in the brain
- PMID: 39048830
- PMCID: PMC11306101
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07745-x
Human TMEFF1 is a restriction factor for herpes simplex virus in the brain
Abstract
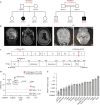
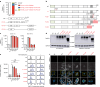
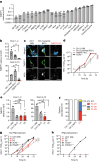
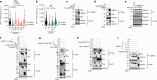
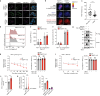
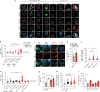
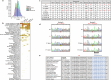
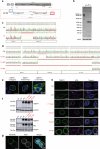
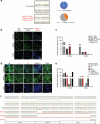
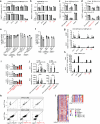
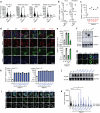
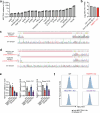
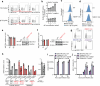
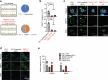
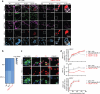
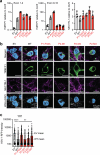
Most cases of herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) encephalitis (HSE) remain unexplained1,2. Here, we report on two unrelated people who had HSE as children and are homozygous for rare deleterious variants of TMEFF1, which encodes a cell membrane protein that is preferentially expressed by brain cortical neurons. TMEFF1 interacts with the cell-surface HSV-1 receptor NECTIN-1, impairing HSV-1 glycoprotein D- and NECTIN-1-mediated fusion of the virus and the cell membrane, blocking viral entry. Genetic TMEFF1 deficiency allows HSV-1 to rapidly enter cortical neurons that are either patient specific or derived from CRISPR-Cas9-engineered human pluripotent stem cells, thereby enhancing HSV-1 translocation to the nucleus and subsequent replication. This cellular phenotype can be rescued by pretreatment with type I interferon (IFN) or the expression of exogenous wild-type TMEFF1. Moreover, ectopic expression of full-length TMEFF1 or its amino-terminal extracellular domain, but not its carboxy-terminal intracellular domain, impairs HSV-1 entry into NECTIN-1-expressing cells other than neurons, increasing their resistance to HSV-1 infection. Human TMEFF1 is therefore a host restriction factor for HSV-1 entry into cortical neurons. Its constitutively high abundance in cortical neurons protects these cells from HSV-1 infection, whereas inherited TMEFF1 deficiency renders them susceptible to this virus and can therefore underlie HSE.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

