Ubiquitination and deubiquitination in cancer: from mechanisms to novel therapeutic approaches
- PMID: 39048965
- PMCID: PMC11270804
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-024-02046-3
Ubiquitination and deubiquitination in cancer: from mechanisms to novel therapeutic approaches
Abstract
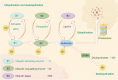
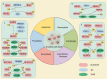
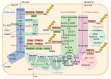
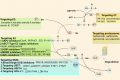
Ubiquitination, a pivotal posttranslational modification of proteins, plays a fundamental role in regulating protein stability. The dysregulation of ubiquitinating and deubiquitinating enzymes is a common feature in various cancers, underscoring the imperative to investigate ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinases (DUBs) for insights into oncogenic processes and the development of therapeutic interventions. In this review, we discuss the contributions of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) in all hallmarks of cancer and progress in drug discovery. We delve into the multiple functions of the UPS in oncology, including its regulation of multiple cancer-associated pathways, its role in metabolic reprogramming, its engagement with tumor immune responses, its function in phenotypic plasticity and polymorphic microbiomes, and other essential cellular functions. Furthermore, we provide a comprehensive overview of novel anticancer strategies that leverage the UPS, including the development and application of proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) and molecular glues.
Keywords: Cancer hallmarks; Immunotherapies; Molecular mechanisms; Targeted therapies; Ubiquitination.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Proteasome substrate receptors and their therapeutic potential.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Nov;47(11):950-964. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.06.006. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35817651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular parameters shaping pathways of targeted protein degradation.Commun Biol. 2025 May 2;8(1):691. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08104-w. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40316744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) as a target for anticancer treatment.Arch Pharm Res. 2020 Nov;43(11):1144-1161. doi: 10.1007/s12272-020-01281-8. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Arch Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 33165832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitination and deubiquitination: Implications on cancer therapy.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2023 Dec;1866(4):194979. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2023.194979. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2023. PMID: 37633647 Review.
-
Hidden targets of ubiquitin proteasome system: To prevent diabetic nephropathy.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Jun;120:170-179. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.03.024. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28363724 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-Translational Modifications of Proteins Orchestrate All Hallmarks of Cancer.Life (Basel). 2025 Jan 18;15(1):126. doi: 10.3390/life15010126. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39860065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitination-mediated upregulation of glycolytic enzyme MCT4 in promoting astrocyte reactivity during neuroinflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Apr 30;22(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03453-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 40307809 Free PMC article.
-
PARylation-mediated post-transcriptional modifications in cancer immunity and immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 11;16:1537615. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1537615. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40134437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of TRIM37 by ATF6 and degradation of ACSL4: inhibiting ferroptosis and propelling cervical cancer progression.Hereditas. 2025 Mar 29;162(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00404-9. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 40158112 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the multifaceted functions of TRIM proteins in glioma pathogenesis.Transl Oncol. 2025 Aug;58:102419. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102419. Epub 2025 May 26. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40424933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

