A self-assessment maturity matrix to support large-scale change using collaborative networks in the New Zealand health system
- PMID: 39049084
- PMCID: PMC11271159
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-024-11284-6
A self-assessment maturity matrix to support large-scale change using collaborative networks in the New Zealand health system
Abstract
Background: A maturity matrix can be a useful tool for organisations implementing large-system transformation (LST) initiatives in complex systems. Insights from implementation of a local LST initiative using collaborative networks, known as Alliances, highlighted a tool was needed to help health system leaders prompt discussions on how and where to focus their change efforts. In the New Zealand (NZ) health system, Alliances were introduced to integrate the planning and delivery of health care between primary and hospital care.
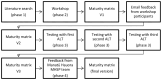
Methods: The aim of this research was to use insights from Alliance members to develop a learning tool that collaborative networks could use to assess and improve their readiness for change. We constructed a maturity matrix using the knowledge of senior NZ health system leaders, in a workshop setting. The maturity matrix was empirically tested and refined with three Alliances and with feedback from the NZ Ministry of Health Māori Health Strategy and Policy team.
Results: The maturity matrix described the 10 key elements that had been found to support successful implementation of LST initiatives in the NZ health system, along with success indicators and different stages of maturity from beginning to excellence. Testing of the maturity matrix with three Alliances suggested that it functioned as a learning tool and stimulated collective thinking and reflection. The Māori Health Strategy and Policy team commented on the importance of such a tool to increase health system leaders' responsiveness to improving Māori health outcomes. Comparisons with similar international matrices revealed common elements with ours. A strength of our maturity matrix is that it is specific to the NZ context and is the first practical tool to implement large-scale change in the health system that incorporates principles of the Government's treaty with Māori, the indigenous people of NZ.
Conclusions: Through a regular self-assessment process, use of the maturity matrix may create feedback loops to support deliberate learning and knowledge sharing for senior health system leaders and collaborative networks. The maturity matrix fills an important gap in the NZ health system and contributes to implementation science literature internationally.
Other: This study was approved by the Victoria University of Wellington Human Ethics Committee (Ethics Approval Number 27,356). The research was supported by the Victoria University of Wellington research grant (222,809) and from the University of Auckland Department of Medicine research fund (H10779).
Keywords: Collaborative networks; Continuous improvement; Health care reform; Integrated care; Large-scale change; Maturity matrix.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
KMS and PBJ were employed by the NZ Ministry of Health and led the design and implementation of the System Level Measures programme referenced in the research. JC and LM do not have any competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Key elements and contextual factors that influence successful implementation of large-system transformation initiatives in the New Zealand health system: a realist evaluation.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Jan 10;24(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-10497-5. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 38200522 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons learnt from the implementation of new models of care delivery through alliance governance in the Southern health region of New Zealand: a qualitative study.BMJ Open. 2022 Oct 31;12(10):e065635. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-065635. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36316079 Free PMC article.
-
A maturity grid assessment tool for learning networks.Learn Health Syst. 2020 Jun 26;5(2):e10232. doi: 10.1002/lrh2.10232. eCollection 2021 Apr. Learn Health Syst. 2020. PMID: 33889737 Free PMC article.
-
Large-system transformation in health care: a realist review.Milbank Q. 2012 Sep;90(3):421-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-0009.2012.00670.x. Milbank Q. 2012. PMID: 22985277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Working Together to Support Self-Determination for Tāngata Kāpō (Blind and Low Vision) Māori: An Exemplar.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Mar 14;21(3):343. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21030343. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38541343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Edwards A, Rhydderch M, Engels Y, Campbell S, Vodopivec-Jamsek V, Marshall M, et al. Assessing organisational development in European primary care using a group-based method: a feasibility study of the Maturity Matrix. Int J Health Care Qual Assur. 2010;23(1):8–21. 10.1108/09526861011010640 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Elwyn G, Bekkers M, Tapp L, Edwards A, Newcombe R, Eriksson T, et al. Facilitating organisational development using a group-based formative assessment and benchmarking method: design and implementation of the International Family Practice Maturity Matrix. Qual Saf Health Care. 2010;19(6):e48. - PubMed
-
- Buch M, Edwards A, Eriksson T. Participants’ evaluation of a group-based organisational assessment tool in Danish general practice: the Maturity Matrix. Qual Prim Care. 2009;17(5):311–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous