Proteolysis of mitochondrial calpain-13 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 39050013
- PMCID: PMC11267081
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101768
Proteolysis of mitochondrial calpain-13 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
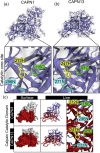
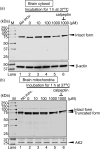
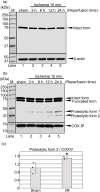
Calpains are calcium-dependent cysteine proteases activated by intracellular Ca2+. Although calpains mainly exist in the cytosol, calpain-13 is present in the mitochondria in mouse brains; however, the enzymatic properties and physiological functions of calpain-13 remain unknown. Hence, in this study, we predicted and evaluated the enzymatic properties of calpain-13. Based on our bioinformatic approaches, calpain-13 possessed a catalytic triad and EF-hand domain, similar to calpain-1, a well-studied calpain. Therefore, we hypothesized that calpain-13 had calpain-1-like enzymatic properties; however, calpain-13 was not proteolyzed in C57BL/6J mouse brains. Subsequently, cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury caused proteolysis of mitochondrial calpain-13. Thus, our study showed that mitochondrial calpain-13 was proteolyzed in the mitochondria of the I/R injured mouse brain. This finding could be valuable in further research elucidating the involvement of calpain-13 in cell survival or death in brain diseases, such as cerebral infarction.
Keywords: Calcium; Calpain catalytic domain; Calpain-13; Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury; Mitochondrion; Mouse brain.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Hosseini M., Najmabadi H., Kahrizi K. Calpains: diverse functions but enigmatic, arch. Iran. Méd. 2018;21:170–179. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

