Towards energy efficiency: A comprehensive review of deep learning-based photovoltaic power forecasting strategies
- PMID: 39050417
- PMCID: PMC11268202
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33419
Towards energy efficiency: A comprehensive review of deep learning-based photovoltaic power forecasting strategies
Abstract
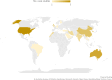
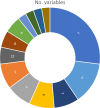
Time series forecasting still awaits a transformative breakthrough like that happened in computer vision and natural language processing. The absence of extensive, domain-independent benchmark datasets and standardized performance measurement units poses a significant challenge for it, especially for photovoltaic forecasting applications. Additionally, since it is often time domain-driven, a plethora of highly unique and domain-specific datasets were produced. The lack of uniformity among published models, developed under diverse settings for varying forecasting horizons, and assessed using non-standardized metrics, remains a significant obstacle to the progress of the field as a whole. To address these issues, a systematic review of the state-of-the-art literature on prediction tasks is presented, collected from the Web of Science and Scopus databases, published in 2022 and 2023, and filtered using keywords such as "photovoltaic," "deep learning," "forecasting," and "time series." Finally, 36 case studies were selected. Before comparing, a state-of-the-art demonstration of key elements in the topic was presented, such as model type, hyperparameters, and evaluation metrics. Then, the 36 articles were compared in terms of statistical analysis, including top publishing countries, data sources, variables, input, and output horizon, followed by an overall model comparison demonstrating every proposed model categorized into model type (artificial neural network units, recurrent units, convolutional units, and transformer units). Due to the mostly utilization of specific private datasets measured at the targeted location, having universal error metrics is crucial for clear global benchmarking. Root Mean Squared Error and Mean Absolute Error were the most utilized metrics, although they specifically demonstrate the accuracy relative to their respective sites. However, 33% utilized universal metrics, such as Mean Absolute Percentage Error, Normalized Root Mean Squared Error, and the Coefficient of Determination. Finally, trends, challenges, and future research were highlighted for the relevant topic to spotlight and bypass the current challenges.
Keywords: Convolutional neural network; Deep learning; Long-short-term memory; Photovoltaic power forecasting; Time series; Transformer.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures












References
-
- Mišík M. The EU needs to improve its external energy security. Energy Policy. 2022;165 doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112930. - DOI
-
- Heng J., Wang J., Xiao L., Lu H. Research and application of a combined model based on frequent pattern growth algorithm and multi-objective optimization for solar radiation forecasting. Appl. Energy. 2017;208:845–866. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.09.063. - DOI
-
- Masson G., de l'Epine M., Kaizuka I. 2023. Trends in PV applications 2023. Tech. Rep., IEA PVPS TCP.
-
- Masson G., Bosch E., Rechem A.V., de l'Epine M. 2023. Snapshot of global PV markets 2023. Tech. Rep., IEA PVPS TCP.
-
- Solar Energy Perspectives OECD. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264124585-en - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

