Global research trends in precision-targeted therapies for systemic lupus erythematosus (2003-2023): A bibliographic study
- PMID: 39050478
- PMCID: PMC11268211
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33350
Global research trends in precision-targeted therapies for systemic lupus erythematosus (2003-2023): A bibliographic study
Abstract
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a persistent inflammatory disease caused by an autoimmune response that predominantly affects multiple organs and systems. Growing evidence highlights the critical role of precision-targeted therapies in the management of SLE. Surprisingly, only a handful of bibliometric studies have thoroughly assessed this area. This study attempts to assess the global landscape of literature output and research trends related to precision-targeted therapy for SLE.
Method: Publications related to precision-targeted therapy for SLE from 2003 to 2023 were searched in the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database. VOSviewers, CiteSpace and the R package "bibliometrix" were used to perform this bibliometric analysis.
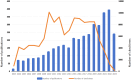
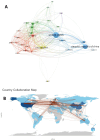
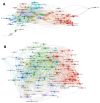
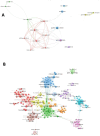
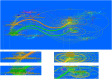
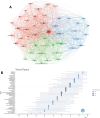
Results: A total of 3700 papers were retrieved, showing a steady annual increase in publications from 2003 to 2022. The United States led the field with the highest number of papers (36.1 %) and secured the top position in terms of citation frequency (59,889) and H-index (115). Anhui Medical University System claimed the top spot with an impressive output of 70 papers. Principal investigators Tsokos, George C. C., and Lu, Qianjin led the research effort. Among the journals, Frontiers in Immunology stood out, publishing the highest number of articles with 191. In particular, precision-targeted therapy for SLE has become a major research focus in recent years, covering aspects such as T cells, B cells, oxidative stress, remission, and PHASE-III.
Conclusion: This bibliometric study of ours systematically analyses research trends in precision targeted therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus, and this information identifies the research frontiers and hot directions in recent years and will serve as a reference for scientists working on targeted therapies.
Keywords: Bibliometric analysis; Citespace; Systemic lupus erythematosus; Targeted therapy; VOSviewers.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Xinchang Wang reports financial support was provided by The Second Affiliated Hospital of 10.13039/501100004863Zhejiang Chinese Medical University. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeted therapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a bibliometric analysis of 2004-2024.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 20;12:1543571. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1543571. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40182841 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of global literature productivity in systemic lupus erythematosus from 2013 to 2022.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Jan;43(1):175-187. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06728-z. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 37668951
-
Microbial dysbiosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: a scientometric study.Front Microbiol. 2024 May 28;15:1319654. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1319654. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38863759 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge Mapping of Exosomes in Autoimmune Diseases: A Bibliometric Analysis (2002-2021).Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 22;13:939433. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.939433. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35935932 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends of the aetiology of systemic lupus erythematosus in the past 10 years: a bibliometric analysis (2014-2023).Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2025 May 1. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/yvqg5k. Online ahead of print. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40314992
Cited by
-
Targeted therapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a bibliometric analysis of 2004-2024.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 20;12:1543571. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1543571. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40182841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kiriakidou M., Ching C.L. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020;172:ITC81–ITC96. - PubMed
-
- Durcan L., O'Dwyer T., Petri M. Management strategies and future directions for systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. Lancet. 2019;393:2332–2343. - PubMed
-
- Bernatsky S., Boivin J.F., Joseph L., Manzi S., Ginzler E., Gladman D.D., Urowitz M., Fortin P.R., Petri M., Barr S., Gordon C., Bae S.C., Isenberg D., Zoma A., Aranow C., Dooley M.A., Nived O., Sturfelt G., Steinsson K., Alarcón G., Senécal J.L., Zummer M., Hanly J., Ensworth S., Pope J., Edworthy S., Rahman A., Sibley J., El-Gabalawy H., McCarthy T., Pierre Y.S., Clarke A., Ramsey-Goldman R. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2550–2557. - PubMed
-
- Kasitanon N., Magder L.S., Petri M. Predictors of survival in systemic lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltim.) 2006;85:147–156. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

