UPLC-ESI-TOF MS Profiling Discriminates Biomarkers in Authentic and Adulterated Italian Samples of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.)
- PMID: 39050589
- PMCID: PMC11265267
- DOI: 10.1021/acsfoodscitech.4c00340
UPLC-ESI-TOF MS Profiling Discriminates Biomarkers in Authentic and Adulterated Italian Samples of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.)
Abstract
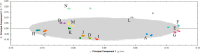
Italian saffron (Crocus sativus L.) is gaining visibility due to its high quality and difference in growing area. In this study, the metabolite composition and quality of Italian saffron samples purchased from local producers and supermarkets were investigated using an untargeted metabolomics approach using UPLC-ESI-TOF MS with simultaneous acquisition of low- and high-collision energy mass spectrometry (MSe). Unsupervised statistical method (PCA) highlighted significant differences in the metabolomes, even if not related to the geographical origin. OPLS-DA revealed 9(S)-,10-(S)-,13-(S)-tri-hydroxy-11-(E)-octadecenoic acid as the most decisive compound to distinguish supermarket saffron, while oxidized crocins represented the most valuable markers to further describe the quality of saffron, even in locally produced samples. Known adulterations with paprika and turmeric were detected at a limit of 10%, and the increasing signals of cyclocurcumin was a significant biomarker for turmeric contamination. The results were underlined with conventional and kinetic antioxidant assays.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






References
-
- Giorgi A.; Pentimalli D.; Giupponi L.; Panseri S. Quality traits of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) produced in the Italian Alps. Open Agric. 2017, 2, 52–57. 10.1515/opag-2017-0005. - DOI
-
- Avula B.; Katragunta K.; Wang Y.-H.; Upton R.; Khan I. A. Analysis of crocetins and safranal variations in saffron (Crocus sativus) stigma samples and dietary supplements using HPLC/UHPLC-PDA-MS: chemical profiling and chemometric analysis using LC-QToF. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 2238–2259. 10.1007/s12161-022-02268-5. - DOI
-
- Zhang A.; Shen Y.; Cen M.; Hong X.; Shao Q.; Chen Y.; Zheng B. Polysaccharide and crocin contents, and antioxidant activity of saffron from different origins. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 133, 111–117. 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.03.009. - DOI
-
- Hegazi N. M.; Khattab A. R.; Frolov A.; Wessjohann L. A.; Farag M. A. Authentication of saffron spice accessions from its common substitutes via a multiplex approach of UV/VIS fingerprints and UPLC/MS using molecular networking and chemometrics. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130739.10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130739. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
