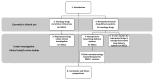
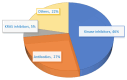
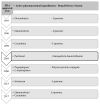
Nonsmall-cell lung cancer treatment: current status of drug repurposing and nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems
- PMID: 39051063
- PMCID: PMC11265851
- DOI: 10.55730/1300-0152.2687
Nonsmall-cell lung cancer treatment: current status of drug repurposing and nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems
Abstract
Drug repurposing is the strategy of drug utilization for a treatment option other than the intended indications. This strategy has witnessed increased adoption over the past decades, especially within cancer nanomedicine. Cancer nanomedicine has been facilitated through nanoparticle-based (NP-based) delivery systems which can combat nonsmall-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) via recent advances in nanotechnology and apply its benefits to existing drugs. The repurposing of drugs, coupled with NP-based drug delivery systems, presents a promising avenue for achieving effective therapeutic solutions with accelerated outcomes. This review aims to present an overview of NSCLC treatments, with a specific focus on drug repurposing. It seeks to elucidate the latest advances in clinical studies and the utilization of NP-based drug delivery systems tailored for NSCLC treatment. First, the molecular mechanisms of Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs for NSCLC, including ROS1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) like repotrectinib, approved in November 2023, are detailed. Further, in vitro studies employing a combination strategy of drug repurposing and NP-based drug delivery systems as a treatment approach against NSCLC are listed. It includes the latest study on nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems loaded with repurposed drugs.
Keywords: Drug repurposing; NSCLC; nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems; nonsmall-cell lung cancer.
© TÜBİTAK.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akinboro O, Larkins E, Pai Scherf LH, Mathieu LN, Ren Y, et al. FDA approval summary: pembrolizumab, atezolizumab, and cemiplimab-rwlc as single agents for first-line treatment of Advanced/Metastatic PD-L1–high NSCLC. Clinical Cancer Research. 2022;28:2221–2228. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3844. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Antonarakis ES, Heath EI, Smith DC, Rathkopf D, Blackford AL, et al. Repurposing itraconazole as a treatment for advanced prostate cancer: a noncomparative randomized phase II trial in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The Oncologist. 2013;18:163–173. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-314. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous