Integrative Metabolomics Differentiate Coronary Artery Disease, Peripheral Artery Disease, and Venous Thromboembolism Risks
- PMID: 39051123
- PMCID: PMC11335080
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.321282
Integrative Metabolomics Differentiate Coronary Artery Disease, Peripheral Artery Disease, and Venous Thromboembolism Risks
Abstract
Background: Arterial and venous cardiovascular conditions, such as coronary artery disease (CAD), peripheral artery disease (PAD), and venous thromboembolism (VTE), are genetically correlated. Interrogating underlying mechanisms may shed light on disease mechanisms. In this study, we aimed to identify (1) epidemiological and (2) causal, genetic relationships between metabolites and CAD, PAD, and VTE.
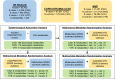
Methods: We used metabolomic data from 95 402 individuals in the UK Biobank, excluding individuals with prevalent cardiovascular disease. Cox proportional-hazards models estimated the associations of 249 metabolites with incident disease. Bidirectional 2-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) estimated the causal effects between metabolites and outcomes using genome-wide association summary statistics for metabolites (n=118 466 from the UK Biobank), CAD (n=184 305 from CARDIoGRAMplusC4D 2015), PAD (n=243 060 from the Million Veterans Project), and VTE (n=650 119 from the Million Veterans Project). Multivariable MR was performed in subsequent analyses.
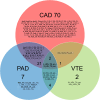
Results: We found that 196, 115, and 74 metabolites were associated (P<0.001) with CAD, PAD, and VTE, respectively. Further interrogation of these metabolites with MR revealed 94, 34, and 9 metabolites with potentially causal effects on CAD, PAD, and VTE, respectively. There were 21 metabolites common to CAD and PAD and 4 common to PAD and VTE. Many putatively causal metabolites included lipoprotein traits with heterogeneity across different sizes and lipid subfractions. Small VLDL (very-low-density lipoprotein) particles increased the risk for CAD while large VLDL particles decreased the risk for VTE. We identified opposing directions of CAD and PAD effects for cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations within HDLs (high-density lipoproteins). Subsequent sensitivity analyses including multivariable MR revealed several metabolites with robust, potentially causal effects of VLDL particles on CAD.
Conclusions: While common vascular conditions are associated with overlapping metabolomic profiles, MR prioritized the role of specific lipoprotein species for potential pharmacological targets to maximize benefits in both arterial and venous beds.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; lipoproteins; vascular disease.
Conflict of interest statement
P. Natarajan reports research grants from Allelica, Amgen, Apple, Boston Scientific, Genentech/Roche, and Novartis; personal fees from Allelica, Apple, AstraZeneca, Blackstone Life Sciences, Creative Education Concepts, CRISPR Therapeutics, Eli Lilly & Co, Foresite Labs, Genentech/Roche, GV, HeartFlow, Magnet Biomedicine, Merck, and Novartis; scientific advisory board membership of Esperion Therapeutics, Preciseli, and TenSixteen Bio; being a scientific cofounder of TenSixteen Bio; equity in MyOme, Preciseli, and TenSixteen Bio; and spousal employment at Vertex Pharmaceuticals, all unrelated to the present work. The other authors report no conflicts.
Figures

Update of
-
Integrative metabolomics differentiate coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and venous thromboembolism risks.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 27:2023.06.21.23291103. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.21.23291103. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Sep;44(9):2108-2117. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.321282. PMID: 37425786 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Mensah GA, Roth GA, Fuster V. The global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors: 2020 and beyond. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:2529–2532. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.10.009 - PubMed
-
- Poredos P, Jug B. The prevalence of peripheral arterial disease in high risk subjects and coronary or cerebrovascular patients. Angiology. 2007;58:309–315. doi: 10.1177/0003319707302494 - PubMed
-
- Aragam KG, Jiang T, Goel A, Kanoni S, Wolford BN, Atri DS, Weeks EM, Wang M, Hindy G, Zhou W, et al. ; Biobank Japan. Discovery and systematic characterization of risk variants and genes for coronary artery disease in over a million participants. Nat Genet. 2022;54:1803–1815. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01233-6 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klarin D, Lynch J, Aragam K, Chaffin M, Assimes TL, Huang J, Lee KM, Shao Q, Huffman JE, Natarajan P, et al. ; VA Million Veteran Program. Genome-wide association study of peripheral artery disease in the Million Veteran Program. Nat Med. 2019;25:1274–1279. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0492-5 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

