Ionic Liquid 1-Octyl-3-Methylimidazolium (M8OI) Is Mono-Oxygenated by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 in Adult Human Liver
- PMID: 39051346
- PMCID: PMC11270251
- DOI: 10.3390/jox14030050
Ionic Liquid 1-Octyl-3-Methylimidazolium (M8OI) Is Mono-Oxygenated by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 in Adult Human Liver
Abstract
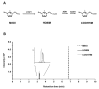
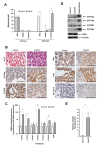
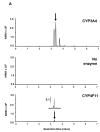
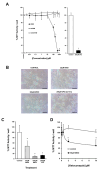
Environmental sampling around a landfill site in the UK previously identified the methylimidazolium ionic liquid, 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium (M8OI), in the soil. More recently, M8OI was shown to be detectable in sera from 5/20 PBC patients and 1/10 controls and to be oxidised on the alkyl chain in the human liver. The objective of this study was to examine the metabolism of M8OI in humans in more detail. In human hepatocytes, M8OI was mono-oxygenated to 1-(8-Hydroxyoctyl)-3-methyl-imidazolium (HO8IM) then further oxidised to 1-(7-carboxyheptyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium (COOH7IM). The addition of ketoconazole-in contrast to a range of other cytochrome P450 inhibitors-blocked M8OI metabolism, suggesting primarily CYP3A-dependent mono-oxygenation of M8OI. Hepatocytes from one donor produced negligible and low levels of HO8IM and COOH7IM, respectively, on incubation with M8OI, when compared to hepatocytes from other donors. This donor had undetectable levels of CYP3A4 protein and low CYP3A enzyme activity. Transcript expression levels for other adult CYP3A isoforms-CYP3A5 and CYP3A43-suggest that a lack of CYP3A4 accounted primarily for this donor's low rate of M8OI oxidation. Insect cell (supersome) expression of various human CYPs identified CYP3A4 as the most active CYP mediating M8OI mono-oxygenation, followed by CYP3A5. HO8IM and COOH7IM were not toxic to human hepatocytes, in contrast to M8OI, and using a pooled preparation of human hepatocytes from five donors, ketoconazole potentiated M8OI toxicity. These data demonstrate that CYP3A initiates the mono-oxygenation and detoxification of M8OI in adult human livers and that CYP3A4 likely plays a major role in this process.
Keywords: C8mim; PBC; cytochrome P450; ionic solvent; methylimidazolium ionic liquids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Leitch A.C., Abdelghany T.M., Probert P.M., Dunn M.P., Meyer S.K., Palmer J.M., Cooke M.P., Blake L.I., Morse K., Rosenmai A.K., et al. The toxicity of the methylimidazolium ionic liquids, with a focus on M8OI and hepatic effects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020;136:111069. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2019.111069. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdelghany T.M., Leitch A.C., Nevjestić I., Ibrahim I., Miwa S., Wilson C., Heutz S., Wright M.C. Emerging risk from “environmentally-friendly” solvents: Interaction of methylimidazolium ionic liquids with the mitochondrial electron transport chain is a key initiation event in their mammalian toxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020;145:111593. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111593. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Probert P.M., Leitch A.C., Dunn M.P., Meyer S.K., Palmer J.M., Abdelghany T.M., Lakey A.F., Cooke M.P., Talbot H., Wills C., et al. Identification of a xenobiotic as a potential environmental trigger in primary biliary cholangitis. J. Hepatol. 2018;69:1123–1135. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.06.027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

